Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How do you calculate the shunt required to increase the length small n times?
Answer in Brief
Solution
- In the arrangement as shown in the figure, I and Ig are the current through the circuit and galvanometer respectively.
Therefore, the current through shunt S is, Is = (I – Ig)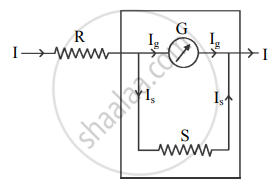
- Since S and G are parallel, the potential difference across them is the same.
∴ GIg = S Is
∴ GIg = S (I - Ig)
∴ S = `(("I"_"g")/("I" - "I"_"g"))"G"` ….(1)
Equation (1) is useful to calculate the range of current that the galvanometer can measure. - If the current I is n times current Ig, then I = n Ig. Using this in equation (1),
S = `(("G""I"_"g")/("n""I"_"g" - "I"_"g"))`
∴ S = `"G"/("n" - 1)`
This is the required shunt to increase the range n times.
shaalaa.com
Is there an error in this question or solution?
