Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How is the structure of DNA organized?
Solution
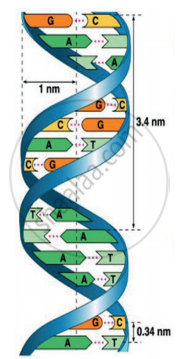
DNA is the hereditary material, as it contains genetic information. It is a large molecule consisting of millions of nucleotides, so it is called a polynucleotide. Each nucleotide consists of three components.
(a) A sugar molecule – Deoxyribose sugar
(b) A nitrogenous base – There are two types of nitrogenous base in DNA they are
- Purines (Adenine and Guanine)
- Pyrimidines (Cytosine and Thymine)
(c) A phosphate group – The polynucleotide chains from a double helix. Nitrogenous bases in the centre are linked to sugar-phosphate units, which form the backbone of the DNA. Pairing between the nitrogenous bases is very specific and is always between purine and pyrimidine, linked by hydrogen bonds.
Adenine (A) links Thymine (T) with two hydrogen bonds [A=T]. Cytosine (C) links Guanine (G) with three hydrogen bonds (C = G). The hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases make the DNA molecule stable. The nucleotides in a helix are joined together by phosphodiester bonds.
Structure of DNA
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name the enzyme and state its property that is responsible for continuous and discontinuous replication of the two strands of a DNA molecule
State whether the following sentence is true or false:
In any specimen of DNA, the total molar amount of A + G = T+ C.
Multiple Choice Question
DNA structure was discovered by:
What happened when heat-killed S-cells along with living R-cells were injected into mice?
The ______ units form the backbone of the DNA.
What is the biological significance of DNA?
Match the Column I with Column II and select the correct option.
| List-I | List-II | ||
| i. | Ribozyme | a. | Lac operon |
| ii. | Friedrich Miescher | b. | DNS as genetic material |
| iii. | Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase | c. | Catalytic RNA molecule |
| iv. | Francois-Jacob | d. | DNA is acidic substance |
Which of the following enzyme catalyse the removal of nucleotides from ends of DNA?
