Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How sex is determined in monoecious plants. write their genes involved in it.
Solution
Zea mays (maize) is an example of monoecious, which means male and female flowers are present on the same plant. There are two types of inflorescence. The terminal inflorescence bears staminate florets that develop from shoot apical meristem called the tassel. The lateral inflorescence which develops pistillate florets from the axillary bud is called ear or cob. Unisexuality in maize occurs through the selective abortion of stamens in-ear florets and pistils in tassel florets. Substitution of two single gene pairs ‘ba’ for barren plant and ‘ts’ for tassel
the seed makes the difference between monoecious and dioecious (rare)
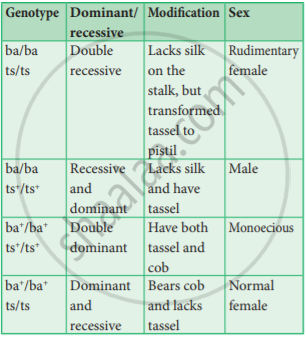
Sex determination in Maize (Superscript (+) denotes dominant character)
maize plants. The allele for barren plant (ba) when homozygous makes the stalk staminate by eliminating silk and ears. The allele for tassel seed
(ts) transforms tassel into a pistillate structure that produces no pollen. The table is the resultant sex expression ‘ based on the combination of these
alleles. Most of these mutations are shown to be defects in gibberellin biosynthesis. Gibberellins play an important role in the suppression of stamens in florets on the ears.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is point mutation? Give one example.
Answer the following question.
Two children, A and B aged 4 and 5 years respectively visited a hospital with a similar genetic disorder. The girl A was provided enzyme-replacement therapy and was advised to revisit periodically for further treatment. The girl, B was, however, given a therapy that did not require revisit for further treatment.
Why did the treatment provided to girl A required repeated visits?
Answer the following question.
Two children, A and B aged 4 and 5 years respectively visited a hospital with a similar genetic disorder. The girl A was provided enzyme-replacement therapy and was advised to revisit periodically for further treatment. The girl, B was, however, given a therapy that did not require revisit for further treatment.
How was the girl B cured permanently?
One of the parents of a cross has mutation in its mitochondria. In that cross, that parent is taken as a male. During segregation of F2 progenies that mutation is found in ______.
A change of single base pair in the gene for beta-globin chain (in human haemoglobin) results in the change of amino acid residue glutamic acid to valine which is due to ______
A strong mutagen is:
Match list I with list II
| List I | List II | ||
| A. | A pair of chromosomes extra with diploid | i) | monosomy |
| B. | One chromosome extra to the diploid | ii) | tetrasomy |
| C. | One chromosome was lost from diploid | iii) | trisomy |
| D. | Two individual chromosomes lose from diploid | iv) | double monosomy |
Match List I with List II.
| List I | List II | ||
| A. | A pair of chromosomes extra with diploid | i) | monosomy |
| B. | One chromosome extra to the diploid | ii) | tetrasomy |
| C. | One chromosome loses from diploid | iii) | trisomy |
| D. | Two individual chromosomes lose from diploid | iv) | double monosomy |
Match list I with list II.
| List I | List II |
| A. A pair of chromosomes extra with diploid | i) Monosomy |
| B. One chromosome extra to the diploid | ii) Tetrasomy |
| C. One chromosome loses a diploid | iii) Trisomy |
| D. Two individual chromosomes lose their diploid | iv) Double chromosome |
Match list I with list II.
| List I | List II | ||
| A. | A pair of chromosomes extra with diploid | i) | monosomy |
| B. | One chromosome extra to the diploid | ii) | tetrasomy |
| C. | One chromosome loses from diploid | iii) | trisomy |
| D. | Two individual chromosomes lose from diploid | iv) | double monosomy |
