Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
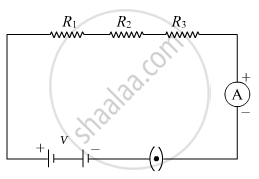
How will you infer with the help of an experiment that the same current flows through every part of the circuit containing three resistors R1, R2 and R3 in series connected to a battery of V volts?
Solution
Consider the given circuit in which a series combination of three resistors of resistances R1, R2 and R3 are shown to be connected to a battery of V volts. An ammeter is also shown to be connected in the circuit. It can be inferred that the current remains the same in the circuit by placing the ammeter at different points in the same circuit i.e. At any point just after R1, R2, and R3. It is observed that the value of the current observed in the ammeter comes to be the same.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Use the data in the Table given below to answer the following –
Which among iron and mercury is a better conductor?
Table give below Electrical resistivity of some substances at 20°C
| Electrical resistivity of some substances at 20°C | ||
| − | Material | Resistivity (Ω m) |
| Conductors |
Silver | 1.60 × 10−8 |
| Copper | 1.62 × 10−8 | |
| Aluminium | 2.63 × 10−8 | |
| Tungsten | 5.20 × 10−8 | |
| Nickel | 6.84 × 10−8 | |
| Iron | 10.0 × 10−8 | |
| Chromium | 12.9 × 10−8 | |
| Mercury | 94.0 × 10−8 | |
| Manganese | 1.84 × 10−6 | |
| Alloys |
Constantan (alloy of Cu and Ni) |
49 × 10−6 |
| Manganin (alloy of Cu, Mn and Ni) |
44 × 10−6 | |
| Nichrome (alloy of Ni, Cr, Mn and Fe) |
100 × 10−6 | |
| Insulators | Glass | 1010 − 1014 |
| Hard rubber | 1013 − 1016 | |
| Ebonite | 1015 − 1017 | |
| Diamond | 1012 − 1013 | |
| Paper (dry) | 1012 | |
Why are alloys commonly used in electrical heating devices? Give reason.
What happens to the resistance as the conductor is made thicker?
Which has more resistance:
a long piece of nichrome wire or a short one?
What do you understand by the "resistivity" of a substance?
Give two examples of substances which are good conductors of electricity. Why do you think they are good conductors of electricity?
How does the resistance of a conductor depend on:
length of the conductor?
What would be the effect on the resistance of a metal wire of:
increasing its temperature?
Calculate the area of cross-section of a wire if its length is 1.0 m, its resistance is 23 Ω and the resistivity of the material of the wire is 1.84 × 10−6 Ω m.
The element used almost exclusively for filaments of incandescent lamps:
