Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Hydroponics have been shown to be a successful technique for growing of plants. Yet most of the crops are still grown on land. Why?
Solution
The nodule contains all the necessary biochemical components, such as the enzyme nitrogenase and leghaemoglobin. The enzyme nitrogenase is a Mo – Fe protein and catalyses the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia, the first stable product of nitrogen fixation.
N2 + 8e– + 8H+ + 16ATP → 2NH3 + H2 + 16ADP + 16P1
- In the above reaction, the ammonia synthesis by nitrogenase requires a very high input of energy (8 ATP for each NH3 produced). The energy required, thus, is obtained from the respiration of the host cells.
The fate of NH3: NH3 produced through N, fixation is incorporated into amino acids as the aniino group. At physiological pH the NH3 is protonated to form \[\ce{NH^{+}4}\] (ammonium) ion. While most of the plants can assimilate \[\ce{NH^{-}3}\] as well as \[\ce{NH^{+}4}\], lions. But \[\ce{NH^{+}4}\] ion is quite toxic to plants, hence cannot accumulate in them
- There are two main ways in which \[\ce{NH^{+}4}\] ion is used to synthesise amino acids in plants:
(I) Reductive amination: In these processes, ammonia reacts with α-ketoglutaric acid and forms glutamic acid as indicated in the equation given below:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{\underset{↓ Glutamate dehydrogenase}{α-ketoglutaric acid + NH^{+}4} + NADPH}\\
\ce{Glutamate + H2O + NADP}
\end{array}\]
(II) Transamination: Transfer of amino group from one amino acid to the keto group of keto acid.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..}\ce{H}\phantom{.........................................................}\ce{H}\phantom{......}\\
\phantom{..}|\phantom{..........................................................}|\phantom{......}\\
\ce{R_1 - C - COO^{-} + R_2 - C - COO^{-} ⇌ R_1 - C - COO^{-} + R_2 - C - COO^{-}}\\
\phantom{................}|\phantom{..................}||\phantom{.........................}||\phantom{..............}|\phantom{....................}\\
\phantom{...................}\ce{\underset{Amino-donor}{NH^{+}3}\phantom{.......}\ce{\underset{Amino-acceptor}{O}}\phantom{...................}\ce{O}\phantom{..............}\ce{NH^{+}3}}\phantom{......................}
\end{array}\]
- Glutamic acid is the main amino acid from which transfer of NH2 (amino group) takes place and other amino acids are formed through transamination. Enzyme transaminase catalyses all such reactions. For example, the two most important amides (asparagine and glutamine) found in plants are a structural part of proteins.
- Asparagine is formed from aspartic acid and glutamine is formed from glutamic acid by the addition of amino groups to each. The hydroxyl part of the acid is replaced by another NH2 radicle.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Why is purification of water and nutrient salts so important in studies involving mineral nutrition using hydroponics?
Growing plants in a nutrient solution on a terrace or balcony are called ______.
Plants obtain their inorganic nutrients from :
Hydroponics is a technique in which plants are grown in ______.
In hydroponics, a suitable mineral solution is prepared by ______.
Carefully observe the following figure
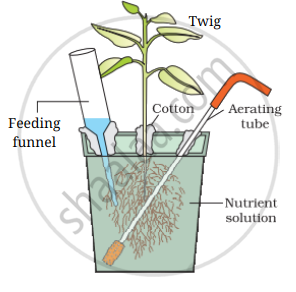
- Name the technique shown in the figure and the scientist who demonstrated this technique for the first time.
- Name atleast three plants for which this technique can be employed for their commercial production.
- What is the significance of aerating tube and feeding funnel in this setup?
