Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
(i)
Write the mathematical expression relating to the variation of the rate constant of a reaction with temperature.
(ii)
How can you graphically find the activation energy of the reaction from the above expression?
(iii)
The slope of the line in the graph of log k (k = rate constant) versus `1/"T"` is -5841. Calculate the activation energy of the reaction.
Solution
(i)
`"k" = "Ae"^(- ("E"_"a")/("RT"))`
k = rate constant
A = collision factor
Ea = activation energy
(ii)
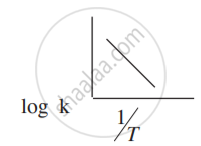
Slope = -`"E"_"a"/(2.303"R")`
(iii)
∴ Ea = – 2.303 × slope × R
= – 2.303 × – 5841 × 8.314
= 111838.4 J mol-1
= 111.8 KJ mol-1
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In a first-order reaction, 10% of the reactant is consumed in 25 minutes. Calculate:
(1) The half-life period of the reaction.
(2) The time required for completing 87.5% of the reaction.
Two moles of NH3 are introduced into the one-litre flask in which it dissociates at high temperature as follows: 2NH3(g) ⇌ N2(g) + 3H2(g). Determine Kc, if at equilibrium 1 mole of NH3 remains.
40% of a first-order reaction is completed in 50 minutes. How much time will it take for the completion of 80% of this reaction?
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word(s) from those given in the brackets:
(two, four, sec-1, diamagnetic, acetaldehyde, mol-1L sec-1, paramagnetic, formaldehyde, acetone, ethanol)
When the concentration of a reactant of first-order reaction is doubled, the rate of reaction becomes ______ times. The unit of rate constant (k) for the first-order reaction is ______.
