Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If there is a convex lens of focal length 75 cm and a concave lens of focal length 40 cm, then calculate their combined power and combined focal length.
Solution
Power of convex lens = `100/("f"("cm"))`
= `100/75` = + 1.33 D.
Power of concave lens = `100/("f"("cm"))`
= `100/40` = − 2.5 D.
Their combined power P = + 1.33 D + (− 2.5 D)
P = − 1.17 D.
Their combined focal length F = `100/"P"=100/(-1.17)`
F = − 85.47 cm.
Negative sign indicates that the nature of their combination is concave.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A convex lens forms a real and inverted image of a needle at a distance of 50 cm from it. Where is the needle placed in front of the convex lens if the image is equal to the size of the object? Also, find the power of the lens.
What is the focal length of a convex lens of focal length 30 cm in contact with a concave lens of focal length 20 cm? Is the system a converging or a diverging lens? Ignore thickness of the lenses.
The focal length of a convex lens is 25 cm. What is its power?
What is the nature of a lens whose power is, −4 D?
The power of a combination of two lenses X and Y is 5 D. If the focal length of lens X be 15 cm :
(a) calculate the focal length of lens Y.
(b) state the nature of lens Y.
The power of a lens is +2.0D. Its focal length should be :
How does focal length of a lens change when red light incident on it is replaced by violet light? Give reason for your answer.
Consider three converging lenses L1, L2 and L3 having identical geometrical construction. The index of refraction of L1 and L2 are \[\mu_1 \text{ and } \mu_2\] respectively. The upper half of the lens L3 has a refractive index \[\mu_1\] and the lower half has \[\mu_2\] following figure . A point object O is imaged at O1 by the lens L1 and at O2 by the lens L2placed in same position. If L3 is placed at the same place,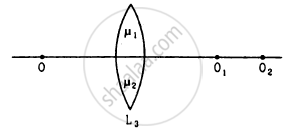
(a) there will be an image at O1
(b) there will be an image at O2.
(c) the only image will form somewhere between O1 and O2
(d) the only image will form away from O2.
A lens forms an upright and diminished image of an object, irrespective of its position. What kind of lens is this? Draw an outline ray diagram to show the formation of the image. State the position and one more characteristic of the image.
Focal length : metre : : power of lens : _______
