Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If you walk from a dark room into sunlight and back again into dark room, how would your pupils alter in size? What makes this happen?
Solution
Initially, in a dark room, the pupil is large so as to allow a large amount of light into the eye. When we go out into sunlight, we feel glare in our eyes as the pupil is large. Gradually, the pupil contracts, and we are able to see clearly. On moving back from sunlight to a dark room again, we are not able to see the surroundings clearly, because the pupil is small. Gradually, the pupil expands, which then improves our vision. This action of the pupil is controlled by the iris, which automatically adjusts the size of the pupil according to the intensity of light that the eye receives.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The optical prescription for a pair of spectacles is :
Right eye : −3.50 D
Left eye : −4.00 D
Which lens has a greater focal length?
Name the part of the eye:
which changes the focal length of eye-lens.
What shape are your eye-lenses:
when you look at your hand?
Which of the following have a wider field of view?
(a) Animals having two eyes on the opposite sides of their head.
(b) Animals having two eyes at the front of their head.
Name the following:
The photoreceptors found in the retina of the eye.
Mention, if the following statement is True or False
Cones are the receptor cells in the retina of the eye sensitive to dim light.
Choose the Odd One Out:
Write the name.
The part of human eye that transmits electrical signals to the brain.
Match the following
| 1. | Conjunctiva | a. | Coloured part of eye |
| 2. | Cornea | b. | Photosensitive layer |
| 3. | Iris | c. | Refraction |
| 4. | Retina | d. | Protection |
Given below is a cross section of the human eye. Match the structures marked (a) to (e) with their correct functions:
Example: (f) - 6. Holds the lens in position
| Cross section of Human Eye | Functions | |
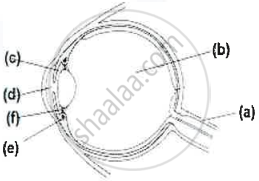 |
1. | Protects retina |
| 2. | Regulates the size of the pupil | |
| 3. | Alters the shape of the lens | |
| 4. | Keeps the lens moist | |
| 5. | Transmits nerve impulses to brain | |
| 6. | Holds the lens in position |
