Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the diagram below, A, B, C, D are four pendulums suspended from the same elastic string PQ. The length of A and C are equal to each other while the length of pendulum B is smaller than that of D. Pendulum A is set into a mode of vibrations

1) Name the type of vibrations taking place in pendulums B and D?
2) What is the state of pendulum C?
3) State the reason for the type of vibrations in pendulum B and C.
Solution
1) The vibrations which occur in pendulums B and D are called forced vibrations.
2) Pendulum C is in the state of resonance with pendulum A as it is of the same length.
3) The pendulums vibrate because the forced vibration from A is transferred due to string PQ
Pendulum B is of a different length as compared to pendulum A. Hence, it will continuously vibrate with a frequency which is different from that of pendulum A. Its amplitude will also be very small.
Pendulum C is of the same length as compared to pendulum A. Hence, it will vibrate in phase with pendulum A. Its amplitude will be equal to that of pendulum A as it will attain resonance
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In following figure shows two tuning forks A and B of the same frequency mounted on two separate sound boxes with their open ends facing each other. The fork A is set into vibration.
- Describe your observation.
- State the principle illustrated by this experiment.

A vibrating tuning fork, held over an air column of a given length with its one end closed, produces a loud audible sound. Name the phenomenon responsible for it and explain the observation.
Why are the stringed instruments like guitar provided with a hollow sound box?
In fig. shows two tuning forks P and Q of the same frequency mounted on separate sound boxes with their open ends facing each other. The fork A is set into vibration. (i) Describe your observation. (ii) State the principle illustrated by this experiment.

The diagram below shows three different modes of vibration P, Q and R of the same string of a given length.
 |
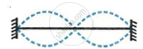 |
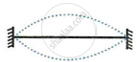 |
| P | Q | R |
- Which vibration will produce a louder sound and why?
- Which vibration will produce sound of maximum shrillness (or pitch) and why?
- What is the ratio of wavelength of vibrations P and R?
A bucket kept under a running tap is getting filled with water. A person sitting at a distance is able to get an idea when the bucket is about to be filled.
(i) What change takes place in the sound to give this idea?
(ii) What causes the change in the sound?
Give two examples of forced vibrations.
State two ways in which resonance differs from forced vibrations.
