Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the figure shown, an ammeter A and a resistor of 4 Ω are connected to the terminals of the source. The emf of the source is 12 V having an internal resistance of 2 Ω. Calculate the voltmeter and ammeter readings.
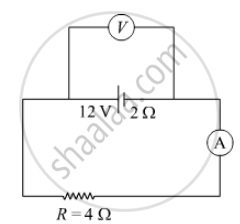
Solution

Considering voltmeter and ammeter to be ideal. Then
Ammeter reading will be,
`I = 12/(4 + 2)`
`= 2 A`
Voltmeter reading will be,
V = 12 − I × 2
= 12 − 2 × 2
=8 V
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw a schematic diagram and explain the working of Van de Graff generator device.
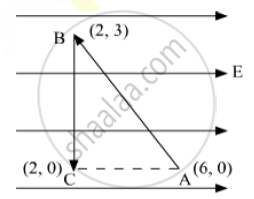
A test charge ‘q’ is moved without acceleration from A to C along the path from A to B and then from B to C in electric field E as shown in the figure. (i) Calculate the potential difference between A and C. (ii) At which point (of the two) is the electric potential more and why?
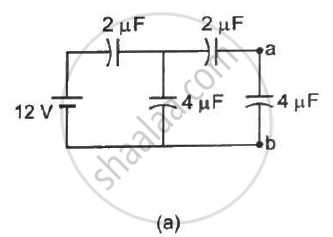
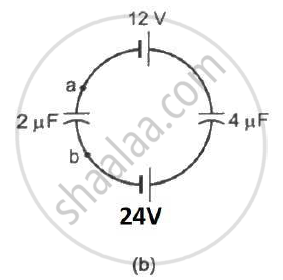
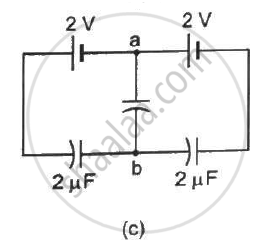
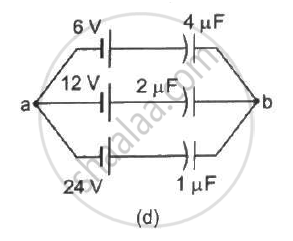
Find the potential difference `V_a - V_b` between the points a and b shown in each part of the figure.
Find the potential difference between the points A and B and between the points B and C of the figure in steady state.

A charge of 20 µC is placed on the positive plate of an isolated parallel-plate capacitor of capacitance 10 µF. Calculate the potential difference developed between the plates.
A charge of 1 µC is given to one plate of a parallel-plate capacitor of capacitance 0⋅1 µF and a charge of 2 µC is given to the other plate. Find the potential difference developed between the plates.
What will be the potential difference in the circuit when direct current is passed through the circuit?
- It depends only on the initial and final position.
- It is the work done per unit positive charge in moving from one point to other.
- It is more for a positive charge of two units as compared to a positive charge of one unit.
A bullet of mass of 2 g is having a charge of 2 µc. Through what potential difference must it be accelerated, starting from rest, to acquire a speed of 10 m/s.
Work done in moving a unit positive charge through a distance of x meter on an equipotential surface is:-
