Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the light of Griffith’s experiment, explain the action of two stains of Diplococcus pneumoniae and give his conclusion.
Solution
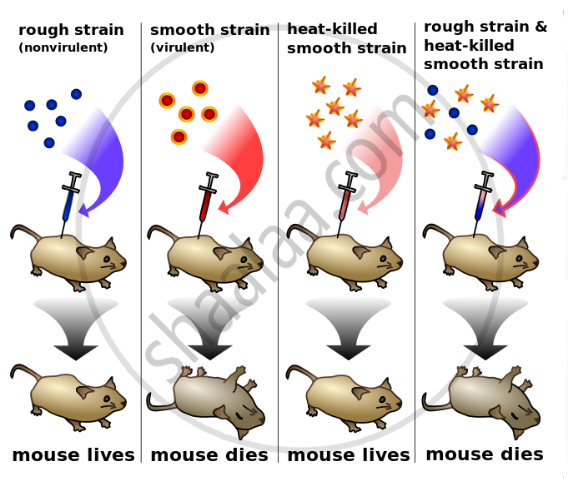
Griffith Experiment: The first series of experiments was performed by a British physician, F. Griffith, in 1928, using the bacterium Diplococcus pneumoniae, which causes pneumonia in mammals.
There are two types of strains;
- S-type is capsulated and smooth and
- R-type is non - capsulated and rough.
When S-type of bacteria were injected into healthy mice, the mice developed pneumonia and died. Thus type of bacteria were injected into healthy mice, and the mice developed pneumonia and died. Thus S-type is virulent or pathogenic. When R-type bacteria were injected into healthy mice, they did not cause pneumonia. Thus R-type is avirulent or non-pathogenic.
Conclusion: Griffith concluded that living R-type bacteria must have picked up something from the surrounding medium that contains heat-killed S-type, and got changed to S-type. This change is due to the phenomenon of transformation. He named that something as a transforming principle. It was later proved that this transforming principle is DNA.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What type of isotopes used in semiconservative replication experiment?
Genetic material in HIV is in the form of ____________.
Which of the following was used by Hershey and Chase to provide the unambiguous proof that DNA is the genetic material?
What would happen if we inject a mice with the mixture of heat killed S-type and living R-type?
Identify the amino acids that are majorly present in histones.
Who proved that DNA is basic genetic material?
The experiments by Hershey and Chase helped confirm that DNA was the hereditary material on the basis of the finding that ______.
What will happen if the double-stranded RNA is produced during transcription?
Classify the following to form Column B as per the category given m Column A:
(i) UUU, (ii) CUA, (iii) UAA, (iv) AUG, (v) UAG, (vi) UGA
| Column 'A' | Column 'B' | |
| (1) | Initiator codon | |
| (2) | Stop codons | |
| (3) | Codon that codes for phenylalanin | |
| (4) | Codon that codes for leucine |
Describe Griffith's transformation experiment.
