Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Let f: R → R be a function defined by f(x) = (x – 3)n1(x – 5)n2, n1, n2 ∈ N. Then, which of the following is NOT true?
Options
For n1 = 3, n2 = 4, there exists α ∈ (3, 5) where f attains local maxima.
For n1 = 4, n2 = 3, there exists α ∈ (3, 5) where f attains local maxima.
For n1 = 3, n2 = 5, there exists α ∈ (3, 5) where f attains local maxima.
For n1 = 4, n2 = 6, there exists α ∈ (3, 5) where f attains local maxima.
Solution
For n1 = 3, n2 = 5, there exists α ∈ (3, 5) where f attains local maxima.
Explanation:
Given: `f(x) = (x – 3)^(n_1)(x – 5)^(n_2)`
⇒ `f^′(x) = (x - 3)^(n_1){n_2(x - 5)^(n_2-1)} + (x - 5)^(n_2){n_1(x - 3)^(n_(1-1))}`
⇒ `f^′(x) = (x - 3)^(n_1-1)(x - 5)^(n_2-1){n_2(x - 3) + n_1(x - 5)}`
⇒ `f^′(x) = (x – 3)^(n_1-1)(x - 5)^(n_2-1){(n_1 + n_2)x - 5n_1 + 3n_2)}`
⇒ `f^′(x) = (x - 3)^(n_1-1)(x - 5)^(n_2-1)(n_1+n_2)(x- (5n_1 + 3n_2)/(n_1 + n_2))`
For n1 = 3, n2 = 4
⇒ `f^'(x) = 7(x - 3)^2(x - 5)^3(x - 27/7)`

Since, sign of f′(x) changes from positive to negative at x = `27/7`
∴ f′(x) has local maxima at x = `27/7` ∈ (3, 5)
For n1 = 4, n2 = 3
⇒ `f^'(x) = 7(x - 3)^3(x - 5)^2(x - 29/7)`

Since, sign of f′(x) changes from negative to positive at x = `29/7`
∴ f′(x) has local maxima at x = `29/7` ∈ (3, 5)
For n1 = 3, n2 = 5
⇒ `f^'(x) = 8(x - 3)^2(x - 5)^4(x - 30/8)`

Since, sign of f′(x) changes from negative to positive at x = `30/8`
∴ f′(x) has local maxima at x = `30/8` ∈ (3, 5)
For n1 = 4, n2 = 6
⇒ `f^'(x) = 10(x - 3)^2(x - 5)^5(x - 38/8)`
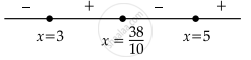
Since, sign of f′(x) changes from negative to positive at x = `38/8`
∴ f′(x) has local maxima at x = `38/8` ∈ (3, 5)
