Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
List the similarities between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Solution
- Energy is produced in both types of respiration.
- Carbon dioxide is produced in both types of respiration.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon dioxide, water, and energy takes place in ______.
What would happen if all the green plants disappear from the earth?
Where in the lungs does gas exchange take place?
State whether the following statement is true or false:
Energy can be produced in cells without oxygen.
Name the type of respiration in which the end product is:
Lactic acid
Give one example where such a respiration can occur.
What is the function of the respiratory system?
Why do the walls of trachea not collapse when there is less air in it?
A, B and C are three living organisms. The organism A is a unicellullar fungus which can live without air. It is used in the commercial production of an organic compound P from molasses. The organism B is a unicellular animal which lives in water and feeds and moves by using pseudopodia. It breathes through an organelle Q. The organism C is a tiny animal which acts as a carrier of malarial parasite. It breathes and respires through a kind of tiny holes R and air-tubes S in its body.
(a) What are organisms (i) A (ii) B, and (iii) C?
(b) Name (i) P (ii) Q (iii) R, and (iv) S.
(c) Which organism/organisms undergo aerobic respiration?
(d) Which organism/organisms undergo anaerobic respiration?
When a person breathes in the air, the air enters into his body through an organ A having two holes B in it. The air then passes through the pharynx and larynx and enters into tube C. The tube C divides into two smaller tubes D at its lower end. The two smaller tubes are attached to two respiratory organs E. Each smaller tube divides inside the organs E to form a large number of still smaller tubes called F. The smallest tubes F have air-sacs G at their ends in which gaseous exchange takes place in the body of the person. What are A, B, C, D, E, F, and G?
Name the body structure concerned with the given functional activity:
Prevents food from entering the trachea during swallowing.
Name the body structure concerned with the given functional activity:
Protects the lungs from mechanical injury
Which chemical compound inside a cell can be termed "Currency of Energy"?
How is the respiratory passage kept free of dust particles?
Air that enters through the nose passes into this tube.
______ refers to the physical process by which gaseous exchange takes place between the atmosphere and the lungs.
How much percent of C02 is transported in a dissolved form as carbonic acid?
What is common between extensive network of blood vessels around walls of alveoli and in glomerulus of nephron?
Explain the three pathways of breakdown in living organisms.
Observe Figure 10.2 carefully and answer the following questions.
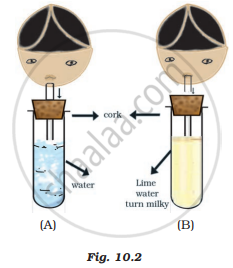
- Which process is being tested in the activity?
- What is the result of the activity? Give reasons.
Match the correct answers with the type of respiration and respiratory substances.
| Respiration | Types of Substrates |
| A. Floating respiration | I. Proteins |
| B. Cytoplasmic respiration | II. Glucose |
| C. Protoplasmic respiration | III. Carbohydrates and fats |
