Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Long answer question.
Explain the classes of carbohydrates with examples.
Solution
Based on number of sugar units, carbohydrates are classified into three types namely, monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
- Monosaccharides:
- Monosaccharides are the simplest sugars having crystalline structure, sweet taste and soluble in water.
- They cannot be further hydrolyzed into smaller molecules.
- They are the building blocks or monomers of complex carbohydrates.
- They have the general molecular formula (CH2O)n, where n can be 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7. e. They can be classified as triose, tetrose, pentose, etc.
- Monosaccharides containing the aldehyde (–CHO) group are classified as aldoses e.g. glucose, xylose, and those with a ketone(–C=O) group are classified as ketoses. E.g. ribulose, fructose.
- Disaccharides:
- Disaccharide is formed when two monosaccharide react by condensation reaction releasing a water molecule. This process requires energy.
- A glycosidic bond forms and holds the two monosaccharide units together.
- Sucrose, lactose and maltose are examples of disaccharides.
- Sucrose is a nonreducing sugar since it lacks free aldehyde or ketone group.
- Lactose and maltose are reducing sugars.
- Lactose also exists in beta form, which is made from β-galactose and β-glucose.
- Disaccharides are soluble in water, but they are too big to pass through the cell membrane by diffusion.
- Polysaccharides:
- Monosaccharides can undergo a series of condensation reactions, adding one unit after the other to the chain till a very large molecule (polysaccharide) is formed. This is called polymerization.
- Polysaccharides are broken down by hydrolysis into monosaccharides.
- The properties of a polysaccharide molecule depends on its length, branching, folding and coiling.
- Examples: Starch, glycogen, cellulose.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the peptide bond.
Answer the following question.
How many types of polysaccharides you know?
Answer the following question.
Explain the induced fit model for the mode of enzyme action.
Answer the following with reference to the following figure.
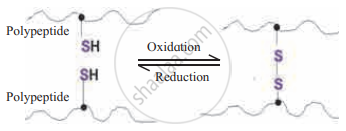
- Name the type of bond formed between two polypeptides.
- Which amino acid is involved in the formation of such bond?
- Amongst I, II, III and IV structural level of protein, which level of structure includes such bond?
Long answer question.
What are biomolecules?
Explain the biomolecules building blocks of life.
Long answer question.
What are the nucleic acids?
Long answer question.
How metabolic pool is formed in the cell.
If double-stranded DNA has 14% C (cytosine) what percent A (adenine), T (thymine) and G (gaunine) would you expect?
Identify the INCORRECT statement with respect to lipids.
