Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Long answer question.
What are the types of RNA? Mention the role of each class of RNA.
Solution
There are three types of cellular RNAs:
- messenger RNA (mRNA),
- ribosomal RNA (rRNA),
- transfer RNA (tRNA).
- Messenger RNA (mRNA):
- It is a linear polynucleotide.
- It accounts 3% of cellular RNA.
- Its molecular weight is several million.
- mRNA molecule carrying information to form a complete polypeptide chain is called cistron.
- Size of mRNA is related to the size of the message it contains.
- Synthesis of mRNA begins at 5’ end of DNA strand and terminates at 3’ end.
Role of messenger RNA:
It carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes, which are the sites of protein synthesis.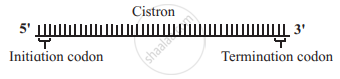
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA):
- rRNA was discovered by Kurland in 1960.
- It forms 50-60% part of ribosomes.
- It accounts 80-90% of the cellular RNA.
- It is synthesized in nucleus.
- It gets coiled at various places due to intrachain complementary base pairing.
Role of ribosomal RNA:
It provides a proper binding site for m-RNA during protein synthesis.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA):
- These molecules are much smaller consisting of 70-80 nucleotides.
- Due to presence of complementary base pairing at various places, it is shaped like clover-leaf.
- Each tRNA can pick up a particular amino acid.
- Following four parts can be recognized on tRNA
1. DHU arm (Dihydroxyuracil loop/ amino acid recognition site
2. Amino acid binding site
3. Anticodon loop/codon recognition site
4. Ribosome recognition site. - In the anticodon loop of tRNA, three unpaired nucleotides are presently called anticodon which pair with codon present on mRNA.
- The specific amino acids are attached at the 3' end in the acceptor stem of clover leaf of tRNA.
Role of transfer RNA:
It helps in the elongation of the polypeptide chain during the process called translation.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Answer the following question.
How many types of polysaccharides you know?
Answer the following question.
What is reducing sugar?
Answer the following question.
Describe the concept of metabolic pool.
Explain the biomolecules building blocks of life.
Long answer question.
Explain the chemical nature, structure and role of phospholipids in the biological membrane.
Long answer question.
Enlist the point of differences among DNA and RNA.
Long answer question.
How metabolic pool is formed in the cell.
Name the form in which carbohydrate is transported in a plant.
Identify the INCORRECT statement with respect to lipids.
The most abundant molecule in cell is ______.
