Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Long answer type question.
Define stress and strain. What are their different types?
Solution
- Stress:
- The internal restoring force per unit area of a body is called stress.
`"Stress" = "deforming force"/"area" = |vec"F"|/"A"`
where `vec"F"` is internal restoring force or external applied deforming force. - Types of stress:
i. Longitudinal stress,
ii. Volume stress,
iii. Shearing stress
- Strain:
- Strain is defined as the ratio of change in dimensions of the body to its original dimensions.
`"Strain" = "change in dimensions"/"original dimensions"` - Types of strain:
i. Longitudinal strain,
ii. Volume strain,
iii. Shearing strain.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Anvils made of single crystals of diamond, with the shape as shown in Figure, are used to investigate the behaviour of materials under very high pressures. Flat faces at the narrow end of the anvil have a diameter of 0.50 mm, and the wide ends are subjected to a compressional force of 50,000 N. What is the pressure at the tip of the anvil?

Answer in one sentence.
Why bridges are unsafe after very long use?
Answer in one sentence.
What is an elastomer?
Answer in one sentence.
What do you mean by elastic hysteresis?
Answer in short.
What do you mean by brittle substance? Give any two examples.
Long answer type question.
Draw a labelled graph of tensile stress against tensile strain for a metal wire up to the breaking point. In this graph show the region in which Hooke’s law is obeyed.
The stress-strain curves are drawn for two different materials X and Y. It is observed that the ultimate strength point and the fracture point are close to each other for material X but are far apart for material Y. We can say that materials X and Y are likely to be (respectively).
The stress-strain graphs for two materials are shown in figure (assume same scale).
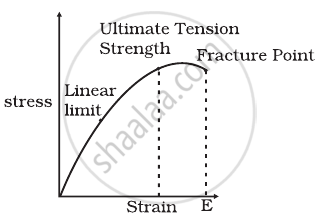 Material (i) |
 Material (i) |
- Material (ii) is more elastic than material (i) and hence material (ii) is more brittle.
- Material (i) and (ii) have the same elasticity and the same brittleness.
- Material (ii) is elastic over a larger region of strain as compared to (i).
- Material (ii) is more brittle than material (i).
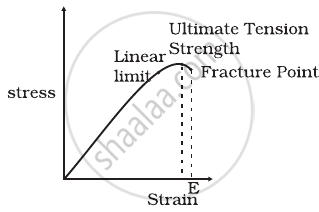
The stress-strain graphs for two materials are shown in figure (assume same scale).
 Material (i) |
 Material (i) |
- Material (ii) is more elastic than material (i) and hence material (ii) is more brittle.
- Material (i) and (ii) have the same elasticity and the same brittleness.
- Material (ii) is elastic over a larger region of strain as compared to (i).
- Material (ii) is more brittle than material (i).
Answer in one sentence:
What is an elastomer?
Answer in one sentence:
What is an elastomer?
Answer in one sentence:
What is an elastomer?
What is an elastomer?
Answer in one sentence:
What is an elastomer?
Answer in one sentence.
What is an elastomer?
Answer in one sentence:
What is an elastomer?
Answer in one sentence:
What is an elastomer?
Answer in one sentence:
What is an elastomer?
