Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Market of a commodity is in equilibrium. Demand for the commodity "increases." Explain the chain of effects of this change till the market again reaches equilibrium. Use diagram.
Explain the chain of effects of ‘increase’ in demand of a good.
Solution
Consider DD to be the initial demand curve and SS to be the supply curve of the market. Market equilibrium is achieved at Point E, where the demand and supply curves intersect each other. Therefore, the equilibrium price is OP, and the equilibrium quantity demanded is OQ.
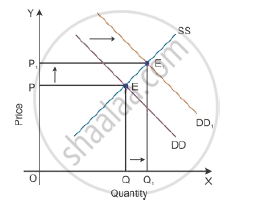
When there is an increase in income of consumers, consumers would tend to spend more on normal goods than the inferior goods where the prices of all goods, tastes and preferences remain constant. There will be a shift in the demand curve towards the right to DD1 with an increase in the demand, and the supply curve SS will remain the same. This implies that at the initial price OP1, there is an excess demand of OQ to OQ1 units at the
initial price OP.
Because of an increase in the demand, there will be an increase in competition among buyers. So, they would be willing to pay more prices to obtain more units of a good in the market. Hence, there will be an increase in the market price to OP2. Now, the new market equilibrium will be at Point E1, where the new demand curve DD1 intersects the supply curve SS.
This clearly states that if the demand curve shifts towards the right, the price of the good tends to increase with an increase in the demand for a good. Thus, the direction of change in equilibrium price and quantity is the same whenever there is a shift in the demand curve.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the law of demand with its assumptions.
State and explain the ‘law of demand’ with its exceptions.
When does ‘increase’ in demand take place?
Distinguish between individuals demand and market demand.
If with the rise in the price of good Y, demand for good X rises, the two goods are: (Choose the correct alternative)
a. Substitutes
b. Complements
c. Not related
d. Jointly demanded
How does change in the price of a substitute good affect the demand of the given good? Explain with the help of an example.
What does a rightward shift of demand curve indicate?
Fill in the blank using proper alternative given in the bracket:
Market demand is a total demand of...............buyers.
Define or explain the following concept.
Market Demand .
State with reason, whether you Agree or Disagree with the following statement.
The demand curve slopes downward from left to right.
Do you agree with the following statement? Give reason
There are no exceptions to the law of demand.
Do you agree with the following statement? Give reason
State and explain the law of demand.
Statements related to decrease in demand
- It is a type of change in demand
- It takes place due to unfavourable changes in other factors like tastes, income etc.
- Price remains constant
- Demand curve shifts to the right hand side of the original demand curve
The shape of supply curve is ______
The demand curve for foreign exchange is ______
Identify the correctly matched items from Column I to that of Column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (1) Demand Curve of Perfect Competition | (a) V-shaped Curve |
| (2) Demand Curve of Monopoly | (b) U-shaped Curve |
| (3) Demand Curve of Monopolistic Competition | (c) Upward rising |
| (4) Demand Curve of Oligopoly | (d) In-determinant |
Assertion (A): The demand curve is downward sloping.
Reason (R): The income effect means with a fall in the price of a good, the consumer's real income or purchasing power rises and he demands more units of the good.
- Assertion (A): The demand curve slopes downwards.
- Reasoning (R): A fall in the price of goods increases the real income of the consumer enabling him/her to buy more.
