Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Match the following
| 1. | Compass | Maximum magnetic strength |
| 2. | Attraction | Like poles |
| 3. | Repulsion | Opposite poles |
| 4. | Magnetic poles | Magnetic needle |
Solution
| 1. | Compass | Magnetic needle |
| 2. | Attraction | Opposite poles |
| 3. | Repulsion | Like poles |
| 4. | Magnetic poles | Maximum magnetic strength |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In which direction does a suspended magnet come to rest?
The following diagrams show two magnets near one another. Use the words, 'Attract, Repel, Turn around' to describe what happens in each case.

Explain the attraction and repulsion between magnetic poles.
You are provided with iron filings and a bar magnet without labelling the poles of the magnet. Using this...
- How will you identify the poles of the magnet?
- Which part of the bar magnet attracts more iron filings? Why?
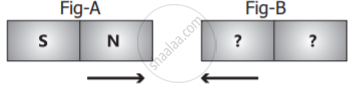
Two bar magnets are given in figure A and B. By the property of attraction, identify the North pole and the South pole in the bar magnet (B)
Where are poles of a bar magnet located?
A bar magnet has no markings to indicate its poles. How would you find out near which end is its north pole located?
The end of the magnet that points to the north is called south pole.
A bar magnet is immersed in a heap of iron filings and pulled out. The amount of iron filling clinging to the
Three identical iron bars are kept on a table. Two out of three bars are magnets. In one of the magnet the North-South poles are marked. How will you find out which of the other two bars is a magnet? Identify the poles of this magnet.
