Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Mention a change which is always desirable.
Solution
Changes that are useful to man are desirable changes, e.g., change of milk into curd.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Suggest a method to liquefy atmospheric gases.
Why is ice at 273 K more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature?
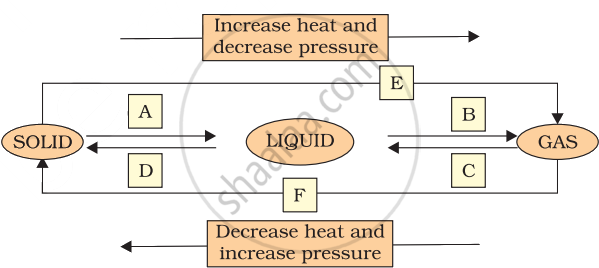
Name A, B, C, D, E and F in the following diagram showing change in its state.
What is the (a) common unit of temperature, and (b) SI unit of temperature ?
Fill in the following blank with suitable words :
The state of matter called ........................ makes a fluorescent tube (or neon sign bulb) to glow.
Why does the temperature remain constant during the boiling of water even though heat is supplied continuously ?
Why does steam cause more severe burns than boiling water ?
Define the following term Melting.
The boiling point of ethane is – 88°C. This temperature will be equivalent to :
When water at 0°C freezes to form ice at the same temperature of 0°C, then it :
The latent heat of vaporisation of water is :
On converting 25°C, 38°C and 66°C to Kelvin scale, the correct sequence of temperatures will be :
Define the following terms: Melting point
Why does a candle become smaller on burning with time?
Write whether the following statement is true or false:
Solids have the larger inter-molecular space
Name the phenomenon which causes the following changes:
Disappearance of camphor when exposed to air
Give two examples of the following:
Substances which sublime.
Give two examples of the following:
Substances which do not change their states.
Give two examples of the following:
Substances which are rigid and not compressible
Fill in the blanks with the correct word/s from the bracket.
Ice on absorption of heat converts to ‘X’ a process called ____ [vaporization / melting]. ‘X’ changes to water vapour on ____ [heating / cooling]. Water vapour changes back to ‘X’ on ____ [freezing / condensation]. The constant temperature at which ice changes into ‘X’ is called its ____ [fusion point / melting point / boiling point].
