Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Name the factors on which the heat produced in a wire depends when current is passed in it, and state how does it depend on the factors stated by you.
Solution
Factors on which heat produced depends:
- On the current of wire: The square of the current l flowing through the wire is directly proportional to the heat H produced by the wire, i.e. H ∝ I2.
- On the resistance of wire: The wire's resistance, R, is directly proportional to the heat, H, that it generates. i.e. H ∝ R.
- On time: The quantity of heat H generated in the wire is proportionate to the duration t. during which current flows through it. i.e. H ∝ t.
From the above, H ∝ I2Rt or H =0.24 I2Rt.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Why are the conductors of electric heating devices, such as bread-toasters and electric irons, made of an alloy rather than a pure metal?
Why does the connecting cord of an electric heater not glow hot while the heating element does?
Explain why, tungsten is used for making the filaments of electric bulbs.
The elements of electrical heating devices are usually made of:
(a) tungsten
(b) bronze
(c) nichrome
(d) argon
The heat produced in a wire of resistance 'x' when a current 'y' flows through it in time 'z' is given by:
(a) x2 × y × z
(b) x × z × y2
(c) y × z2 × x
(d) y × z × x
Solve the following example.
Heat energy is being produced in a resistance in a circuit at the rate of 100 W. The current of 3 A is flowing in the circuit. What must be the value of the resistance?
An electric iron of 1100 W is operated for 2 hrs daily. What will be the electrical consumption expenses for that in the month of April? (The electric company charges Rs 5 per unit of energy).
(a) Observe the diagram given below and state whether the bulb will glow or not when we switch on K.
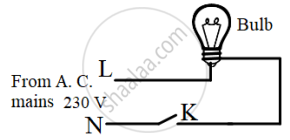
(b) Is it safe to handle the bulb when the switch is OFF?
(c) Give a reason for your answer in (b).
Fuse is a strip of alloy wire which is made up of lead and tin with a very low ______.
Match the following
| 1. | Bulb | a. | Conductor |
| 2. | Electroplating | b. |
Insulator |
| 3. | Pure water | c. | Heating effect of current |
| 4. | Salt solution | d. | Chemical effect of current |
