Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Name the following:
No breathing.
Solution
Apnea
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Differentiate between the following pairs on the basis of the aspect given in the brackets.
Photosynthesis and Respiration (Reactants)
The volume of air in the lungs and the rate at which it is exchanged during inspiration and expiration was measured.
The following diagram shows a group of the lung volumes and capacities.
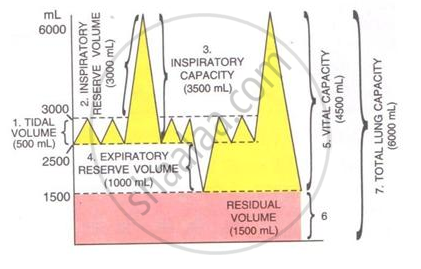
Study the diagram carefully and explain briefly the following :
Residual volume (RV)
Put a tick (✓) against the most appropriate alternative in the following statement.
In humans, taken in of the air through nostrils into the nasal cavity is called
Name the following:
The microscopic air-sacs of the lungs.
Fill in the blank.
The Malpighian body consists of Bowman’s capsule and _____________.
Differentiate between
Bowman’s capsule and alveolus
What are their functions?
Complete the following statement by choosing the correct alternative from those given below.
The protective covering of the lung ______.
What is respiration?
Into which of the following does the terminal bronchiole end?
TV and ERV of an athlete are 500 mL and 1000 mL respectively. What will be his Expiratory Capacity if the RV is 1200 mL?
Bronchi are supported by ____________.
Which of the following has a set of lymphoid organs called tonsils?
A biochemical compound that readily combines with oxygen and distributes it throughout the human body is ____________.
What is the primary organ of the respiratory system?
Pick the odd one out from each of the groups given below on the basis of respiratory organs. Give a reason for your answer.
lizard, cow, earthworm, snake
Which of the following is NOT included in conducting part of the respiratory system?
A person suffers punctures in his chest cavity in an accident without any damage to the lungs. Its effect could be ______.
For completion of respiration process, write the given steps in sequential manner
- Diffusion of gases (O2 and CO2) across alveolar membrane.
- Transport of gases by blood.
- Utilisation of O2 by the cells for catabolic reactions and resultant release of CO2.
- Pulmonary ventilation by which atmospheric air is drawn in and CO2 rich alveolar air is released out.
- Diffusion of O2 and CO2 between blood and tissues.
