Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Name two examples in which the mechanical energy of a system remains constant.
Solution
(1) A body hurled vertically upward under gravity experiences a continuous increase in P.E. and a continuous decrease in KE. The sum of these two quantities at any one time stays constant.
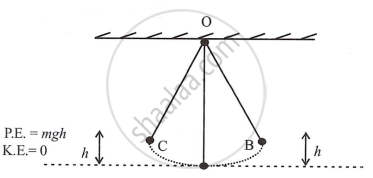
(2) Because of the height h above ground and KE = 0, in the case of a simple pendulum at B, Bob just has P.E.
∴ Sum of P.E. + K.E. = mgh + 0 = mgh
At A the resting position h = 0 and P.E. = 0 but has maximum KE. (Since P.E. has been converted into KE.)
∴ Sum of P.E. and K.E. is same at A as at B.
Now again as bob rises above ground to position C, K.E., decreases to zero and P.E. = mgh
∴ Sum of P.E. and K.E. = mgh
We see that in all three places, P.E. + K.E., i.e., the mechanical energy of the system, remains constant.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define calorific value of a fuel.
Name the type of energy (kinetic or potential) possessed by the following:
A moving cricket ball.
Name three non-renewable sources of energy.
Name the energy changes for the following:
bicycle brakes
A ball of mass 0.5 kg slows down from a speed of 5m/s-1 to that of 3m/s-1. Calculate the change in kinetic energy of the ball.
What kind of energy is possessed in a situation when?
A horse running along a level road
What is dissipation of energy?
Give one example when:
Kinetic energy changes to heat energy.
A girl of mass 35 kg climbs up from the first floor of a building at a height 4 m above the ground to the third floor at a height 12 m above the ground. What will be the increase in her gravitational potential energy? [g = 10 ms-2]
The solar cooker is an application of the ______ energy of the sun, while solar cells, solar lamps are applications of the ______ energy of the sun.
