Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Name two main processes of sexual reproduction
Solution
Two main processes of sexual reproduction:
(1) Meiosis: It is a process of cell division in which the chromosome number is reduced to half to form haploid gametes (2n→n).
(2) Fertilisation: The union of the haploid male gamete with the haploid female gamete to form the diploid zygote is called fertilisation. By fertilisation, the chromosome number again becomes diploid (2n).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Complete the following table to get the differences between asexual and sexual reproduction:
| Characteristics | Asexual Reproduction | Sexual Reproduction |
| Number of parents involved | ........................... | .............................. |
| Type of cells involved | Somatic cells | Germ cells |
| Type of cell division | ............................ | Meiosis and mitosis |
What is meant by sexual reproduction?
List six specific characteristics of sexual reproduction.
No two individuals are absolutely alike in a population. Why?
What is amphimixis?
Oviparous animals give birth to young ones.
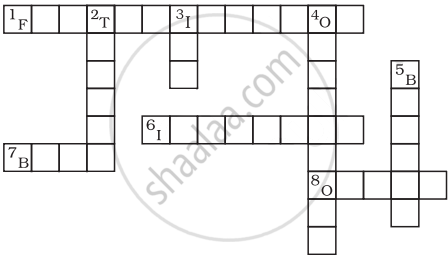
Complete the crossword puzzle using the hints given below.
Across
1. The process of the fusion of the gametes.
6. The type of fertilisation in hen.
7. The term used for bulges observed on the sides of the body of Hydra.
8. Eggs are produced here
Down
2. Sperms are produced in these male reproductive organs.
3. Another term for the fertilised egg.
4. These animals lay eggs.
5. A type of fission in amoeba.
Differentiate between Parthenocarpy and Parthenogenesis. Give one example of each.
What is the other name of sex cells?
What would be the ratio of chromosome number between an egg and its zygote?
Distinguish between the following pair of terms:
Budding and Regeneration.
Define the term Fetilization.
Multiple choice question. Tick (✓) the correct choice:
Which of the following glands is responsible for bringing about changes during adolescence in boys and girls?
- pituitary
- adrenal
- thyroid
- testis
Define the term Puberty.
Mention the common method of reproduction in Amoeba.
Mention the common method of reproduction in Flatworm.
Describe the different methods of asexual reproduction in animals.
How is the chromosome number maintained in sexually reproducing organisms?
Answer the following question.
It is commonly observed that parents feel embarrassed to discuss freely with their adolescent children about sexuality and reproduction. The result of this parental inhibition is that the children go astray sometimes.
Explain the reasons that you feel are behind such embarrassment amongst some parents to freely discuss such issues with their growing children.
Answer in one sentence.
Name the endocrine glands involved in maintaining the sex characteristics of males.
Answer the following question.
Explain the following parts of male reproductive system along with labelled diagram showing these parts- Testis, vasa deferentia, epididymis, seminal vesicle, prostate gland and penis.
What is atresia with respect to ovary in human females?
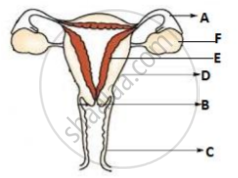
Identify the labels from the given diagram.
Write an account of the seminal vesicle and bulbourethral gland in the male reproductive system.
How is juvenile phase different from reproductive phase?
Identify the correct sequence of events.
In sexual reproduction, offsprings resemble the parents ______.
The end of vegetative phase in plants which marks the beginning of the reproductive phase can be easily seen in the higher plants when they come to ______.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following statements, support the view that elaborate sexual reproductive process appeared much later in the organic evolution.
- Lower groups of organisms have simpler body design
- Asexual reproduction is common in lower groups
- Asexual reproduction is common in higher groups of organisms
- The high incidence of sexual reproduction in angiosperms and vertebrates
Identify the incorrect statement.
What is external fertilisation?
Explain the two types of fertilization.
Mention two inherent characteristics of Amoeba and yeast that enable them to reproduce asexually.
With which type of reproduction do we associate the reduction division? Analyse the reasons for it.
Enumerate the differences between asexual and sexual reproduction. Describe the types of asexual reproduction exhibited by unicellular organisms.
Which is a better mode of reproduction, sexual or asexual? Why?
Explain how stability of the DNA of the species is ensured in sexually reproducing organisms.
