Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why does NH3 form hydrogen bond but PH3 does not?
Solution 1
Nitrogen is highly electronegative as compared to phosphorus. This causes a greater attraction of electrons towards nitrogen in NH3 than towards phosphorus in PH3. Hence, the extent of hydrogen bonding in PH3 is very less as compared to NH3.
Solution 2
Nitrogen has an electronegativity value 3.0, which is much higher than that of H (2.1). As a result, N – H bond is quite polar and hence NH3 undergoes intermolecular H – bonding
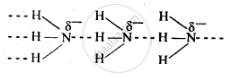
Phosphorus have an electronegativity value 2-1. Thus, P – H bond is not polar and hence PH3 does not undergo H – bonding.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Account for the following: Oxygen shows catenation behavior less than sulphur.
Give reasons for the following : H2Te is the strongest reducing agent amongst all the hydrides of Group 16 elements.
Give reasons for the following : Oxygen has less electron gain enthalpy with negative sign than sulphur.
List the important sources of sulphur.
Write the order of thermal stability of the hydrides of Group 16 elements.
The HNH angle value is higher than HPH, HAsH and HSbH angles. Why? [Hint: Can be explained on the basis of sp3 hybridisation in NH3 and only s−p bonding between hydrogen and other elements of the group].
Justify the placement of O, S, Se, Te and Po in the same group of the periodic table in terms of electronic configuration, oxidation state and hydride formation.
Arrange the following in the order of property indicated for each set:
F2, Cl2, Br2, I2 - increasing bond dissociation enthalpy.
Arrange the following in the order of the property indicated against set :
H2O, H2S, H2Se, H2Te − increasing acidic character.
Explain the following properties of group 16 elements :
1) Electro negativity
2) Melting and boiling points
3) Metallic character
4) Allotropy
Give a reason for the following:
Fluorine gives only one oxide but chlorine gives a series of oxides.
Arrange the following in order of the property indicated set.
HF, HCl, HBr, HI - decreasing bond enthalpy.
The formation of \[\ce{O^+_2[PtF6]^-}\] is the basis for the formation of first xenon compound. This is because ____________.
Match the items of Columns I and II and mark the correct option.
| Column I | Column II |
| (A) \[\ce{H2SO4}\] | (1) Highest electron gain enthalpy |
| (B) \[\ce{CCl3NO2}\] | (2) Chalcogen |
| (C) \[\ce{Cl2}\] | (3) Tear gas |
| (D) Sulphur | (4) Storage batteries |
Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Electron gain enthalpy of oxygen is less than that of Flourine but greater than Nitrogen.
Reason (R): Ionisation enthalpies of the elements follow the order Nitrogen > Oxygen > Fluorine.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction showing catalytic oxidation of NH3 by atmospheric oxygen.
In forming (i) \[\ce{N2 -> N^{+}2}\] and (ii) \[\ce{O2 -> O^{+}2}\]; the electrons respectively are removed from:
Which of the following compound is a peroxide?
These are physical properties of an elements.
- Sublimation enthalpy
- Ionisation enthalpy
- Hydration enthalpy
- Electron gain enthalpy
The total number of above properties that affect the reduction potential is ______. (Integer answer)
What is the basicity of \[\ce{H3PO4}\]?
