Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Observe the figure and label it properly.

- Name the hormone that regulates the cycle.
- Name the phases in this cycle.
- What is the duration of ovulation phase?
- What happens if implantation occurs?
- What happens if implantation does not occur?
Solution

- The menstrual cycle is a natural process, controlled by four hormones. Those four hormones are follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), estrogen, and progesterone.
- The cycle consists of three phases-menstrual phase, the proliferative phase, and secretory phase.
- 14 days.
- If the embryo is implanted, repetition of this cycle is temporarily stopped till the parturition and thereafter period of breastfeeding.
- If oocyte is not fertilized within 24 hours, corpus luteum becomes inactive and transforms into corpus Albicans. Due to this, secretion of estrogen and progesterone stops completely. Endometrium starts to degenerate in absence of these two hormones.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name the function of the following:
Corpus luteum
Give appropriate biological or technical terms for the following:
The onset of menstruation in a young girl
Give appropriate terms for each of the following process:
Fixing of developing zygote (blastocyst) on the uterine wall.
Sketch the labeled diagram:
Menstrual cycle
Define: Menarche
Read the following passage and answer the question that follows:
Rahini and her parents were watching a television programme. An advertisement flashed on the screen which was promoting the use of sanitary napkins. Rahini’s parents suddenly changed the channel, but she objected to her parents and explained the need and importance of such an advertisement.
What is first menstruation called? When does it occur?
Lack of which hormone results in menstrual flow?
All occur during follicular phase of menstrual cycle, EXCEPT
Luteal phase is also known as ____________.
Which set is similar?
Withdrawal of which of the following hormones is the immediate cause of menstruation?
Level of which hormones are at their highest during the luteal phase (second half of the cycle) of the menstrual cycle?
A human female reaches menopause aroung the age of ______.
A biology student after studying the different levels of hormones during the menstrual cycle was comparing 2 subjects (Patients). A table was created after looking at the levels of hormones A and B for Subjects 1 and 2. Read the information in the table and answer the question that follows.
| HORMONE A | HORMONE B | |
| Subject 1 | Shows a peak on the 14th Day of the menstrual cycle. | Falls down during the luteal phase. |
| Subject 2 | Shows a peak on the 14th Day of the menstrual cycle. | The level is maintained high in the luteal phase. |
For subject 2 it is observed that the peak for hormone B has reached the plateau stage. After approximately how much time will the curve for hormone B descend?
The main function of mammalian corpus luteum is to produce ______.
The menstrual cycle begins with ______
A human female experiences two major changes, menarche and menopause during her life. Mention the significance of both the events.
What role does pituitary gonadotropins play during follicular and ovulatory phases of menstrual cycle? Explain the shifts in steroidal secretions.
In the figure given below, parts A and B show the level of hormones which influence the menstrual cycle. Study the figure and answer the questions that follow:
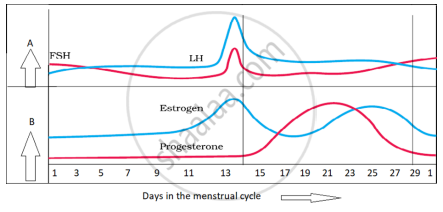
- Name the organs which secrete the hormones represented in parts A and B.
- State the impact of the hormones in part B on the uterus of the human female during 6 to 15 days of the menstrual cycle.
Complete the following table by writing the name of the structure or the function of the given structure:
| Structure | Function | ||
| 1. | Corpus luteum | 1. | ______ |
| 2. | ______ | 2. | Produces male gametes in mass |
| 3. | Leydig cells | 3. | ______ |
| 4. | ______ | 4. | Stores the sperms until they mature and become mobile |
| 5. | Umbilical cord | 5. | ______ |
| 6. | Fallopian tube | 6. | ______ |
