Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Obtain the mirror formula and write the expression for the linear magnification.
Solution
Mirror Formula
`
The above figure shows the ray diagram for image formation by a concave mirror.
In figure triangle A'B'F and ENF are similar.
`∴ (A'B')/(NE) = (A'F)/(NF)`
As the aperture of the concave mirror is small, the points N and P lie very close to each other.
∴ NF ≈ PF and NE = AB
`(A'B')/(AB) = (A'F)/(PF)`
Since all the distances are measured from the pole of the concave mirror, we have
A'F = PA' - PF
`:. (A'B')/(AB) = (PA' - PF)/(PF)` ...(i)
Also, triangles ABP and A'B'P are similar
`:. (A'B')/(AB) = (PA')/(PA)` ....(ii)
Applying the new Cartesian sign conventions, we have
PA = -u (Q distance of the object is measured against incident ray)
PA' = -v (Q distance of image is measured against incident ray)
PF = -f(Q focal length of the concave mirror is measured against incident ray)
Substituting these values in equation (iii),
We have
`(-v-(-f))/(-f) = (-v)/(-u)`
`(v-f)/f = v/u`
`v/f - 1 = v/u` or `1/f - 1/v = 1/u`
`1/u + 1/v = 1/f`
Linear magnification
The ratio of the size of the image formed by a spherical mirror to the size of the object is called the linear magnification produced by the spherical mirror.
It is denoted by m.
`m = I/O = (-v)/u`
Where,
I → Size of the image
O → Size of the object
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Suppose the lower half of the concave mirror's reflecting surface is covered with an opaque material. What effect this will have on the image of the object? Explain
A convex lens of focal length 20 cm is placed coaxially with a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm at a distance of 50 cm apart from each other. A beam of light coming parallel to the principal axis is incident on the convex lens. Find the position of the final image formed by this combination. Draw the ray diagram showing the formation of the image
A convex lens of focal length 20 cm is placed coaxially in contact with a concave lens of focal length 25 cm. Determine the power of the combination. Will the system be converging or diverging in nature?
A convex lens of focal length 25 cm is placed coaxially in contact with a concave lens of focal length 20 cm. Determine the power of the combination. Will the system be converging or diverging in nature?
A convex lens of focal length 30 cm is placed coaxially in contact with a concave lens of focal length 40 cm. Determine the power of the combination. Will the system be converging or diverging in nature?
A convex lens of focal length f1 is kept in contact with a concave lens of focal length f2. Find the focal length of the combination.
An object AB is kept in front of a concave mirror as shown in the figure.
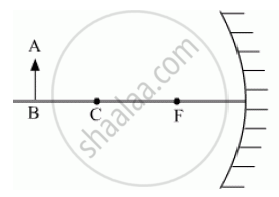
(i) Complete the ray diagram showing the image formation of the object.
(ii) How will the position and intensity of the image be affected if the lower half of the mirror’s reflecting surface is painted black?
A particle is moving at a constant speed V from a large distance towards a concave mirror of radius R along its principal axis. Find the speed of the image formed by the mirror as a function of the distance x of the particle from the mirror.
A mass m = 50 g is dropped on a vertical spring of spring constant 500 N m−1 from a height h = 10 cm as shown in figure. The mass sticks to the spring and executes simple harmonic oscillations after that. A concave mirror of focal length 12 cm facing the mass is fixed with its principal axis coinciding with the line of motion of the mass, its pole being at a distance of 30 cm from the free end of the spring. Find the length in which the image of the mass oscillates.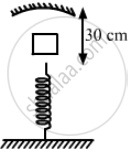
In the case of a concave mirror of focal length f , when an object is kept between f and 2 f , show that its image is formed beyond 2 f .
