Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
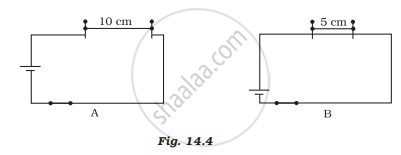
Paheli took a wire of length of 10 cm. Boojho took a wire of 5 cm of the same material and thickness. Both of them connected the wires as shown in the circuit given in Figure 14.4. The current flowing in both circuits is the same.
(i) Will the heat produced in both cases be equal? Explain
(ii) Will the heat produced be the same if the wires taken by them are of equal lengths but of different thicknesses? Explain.
Solution
(i) No, the amount of heat produced in both cases will not be equal. The amount of heat produced in a wire depends upon the length of the wire.
(ii) No, the amount of heat produced in the wire depends upon the thickness of the wire.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Why does the cord of an electric heater not glow while the heating element does?
Name the material which is used for making the filaments of an electric bulb.
Three heaters each rated 250 W, 100 V are connected in parallel to a 100 V supply. Calculate:
- the total current taken from the supply
- the resistance of each heater and
- the energy supplied in kWh to the three heaters in 5 hours.
What is a short circuit?
What is used to turn off the sudden increase in current in the electrical circuit of the house nowadays?
What does overloading cause?
A student boils water in an electric kettle for 20 minutes. Using the same mains supply he wants to reduce the boiling time of water. To do so should he increase or decrease the length of the heating element? Justify your answer.
What is a trip switch?
An electric kettle consumes 1 kW of electric power when operated at 220 V. A fuse wire of what rating must be used for it?
Anannya responded to the question: Why do electrical appliances with metallic bodies are connected to the mains through a three-pin plug, whereas an electric bulb can be connected with a two-pin plug?
She wrote: Three-pin connections reduce heating of connecting wires.
- Is her answer correct or incorrect? Justify.
- What is the function of a fuse in a domestic circuit?
