Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
|
RNA interference (RNAi) holds great potential as a therapeutic agent for the treatment of human diseases and as biocontrol agents in controlling pests in the field agriculture. An experiment was carried to study the use of 'RNAi' for the potential treatment of disorders of cholesterol metabolism. Some people possess genetic mutations with elevated levels of ApoB gene which predisposes them to coronary artery diseases. Lowering the amount ApoB can reduce the number of lipoproteins and lower the blood cholesterol. Tracy Zimmerman and her colleagues used RNAi in 2006 to reduce the level of ApoB in non human primates Cynomolgus monkeys. One group of monkeys were given RNAi treatment (small interfering RNAs, SiRNAs) (doses 1 mg/kg, SiRNAs), second group of monkeys were given RNAi treatment (doses 2.5 mg/kg, SiRNAs) and third group of monkeys were injected with saline. |
The results of the study are depicted in the graph below:
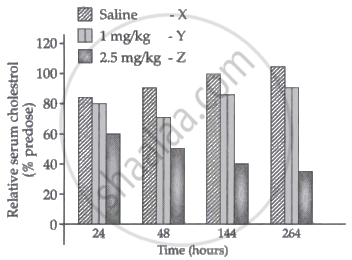
- How does the treatment with 2.5 mg/kg bring an effect on cholesterol metabolism when compared from 24 hours and 144 hours?
- Write any two natural sources from where dsRNA molecule could be obtained for silencing the specific mRNA.
- How is RNAi used in controlling the infection on the roots of tobacco plants by the nematode Meloidogyne incognitia?
Solution
- RNAi treatment has a notable impact in comparison to saline treatment. The Cynomolgus monkeys displayed nearly 60% of relative serum cholesterol throughout the first 24 hours. However, when treated with 2.5 mg/Kg siRNAs, this level of serum cholesterol dramatically dropped by 40% after 144 hours. This indicates that the amount of ApoB protein produced is decreased as the mRNA.
- Natural sources: The source of this complementary RNA could be from infection by viruses having RNA genomes or mobile genetic elements (transposons) that replicate via an RNA intermediate.
- The roots of tobacco plants are infected by the nematode Meloidegyne incognitia, which significantly reduces production. This infestation is stopped using an RNA interference (RNAi) technique. In all eukaryotic organisms, RNAi is used as a cellular defence mechanism. Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) controls the sequence-specific degradation of mRNA throughout this process. Due to a complementary dsRNA molecule, it suppresses (silencing) the translation of a certain mRNA.
The steps of RNA interference are as follows:
- The source of this complementary RNA could be from infection by viruses having RNA genomes or mobile genetic elements (transposons) that replicate via an RNA intermediate.
- Using Agrobacterium vectors, nematode-specific genes were introduced into the host plant.
- The introduction of DNA was such that it produced both sense and anti-sense RNA in the host cells.
- These two RNAs being complementary to each other formed a double-stranded (dsRNA) that initiated RNAi and thus, silenced the specific mRNA of the nematode.
- The consequence was that the parasite could not survive in a transgenic host expressing specific interfering RNA.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the term biofortification. How is this technique useful for the production of ‘ golden rice?
Answer the following question.
List any four ways by which GMOs have been useful for enhanced crop output.
Answer the following question.
Write the desirable characters a farmer looks for in his sugarcane crop.
Which one of the followmg bacterium is used for the production of transgenic plants?
Bt brinjal is an example of transgenic crops. In this Btrefers to ______.
The trigger for activation of toxin of bacillus thuringlensis is ______.
Assertion (A): In Bt cotton, B. thuringiensis produces a toxic insecticidal crystalline protein which destroys bollworms.
Reason (R): B. thuringiensis produces this toxic protein in an inactive form, but when an insect ingests this inactive protein, it is converted into active form of toxin due to the alkaline pH of gut which solubilises the crystals, which is responsible for the death of bollworm.
You have identified a useful gene in bacteria. Make a flow chart of the steps that you would follow to transfer this gene to a plant.
What are cry-proteins?
The main objective of the production of pest-resistant GM crops is to ______.
