Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Sketch the labeled diagram:
Flower with its sexual reproductive organs
Solution
Flower with its sexual reproductive organs

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Answer the following question.
State significance of pollination.
Explain what you understand by sexual reproduction.
Sketch the reproductive parts of a flower.
State the name of the functional unit concerned with sexual reproduction.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
The ovule becomes a .......... after fertilisation.
What is made in ovary of a flower?
What is meant by 'unisexual flowers' and 'bisexual flowers'? Give two examples of each.
Describe the process of fertilisation in a flower with the help of labelled diagrams.
The correct sequence of reproductive stages occurring in flowering plants is ______
The flask-shaped organ A at the centre of a flower is surrounded by a number of little stalks B having swollen tops which lie just inside the ring of petals.
(a) Name A. What are the various parts of A?
(b) Which part of A contains gametes?
(c) Name B. What is the swollen top of B known as?
(d) What does the swollen top of b contain?
(e) Out of A and B, which one is (i) male part, and (ii) female part of the flower?
In a bisexual flower, inspite of the young stamens being removed artificially, the flower produces fruit. Explain.
Fill in the blank by selecting suitable word:
A flower bearing only male or female parts is known as __________ flower.
What is a flower ? Draw a neat labelled diagram showing the L.S. of a typical flower.
Find the odd-one out, giving reason:
Anther, pollen grain, ovule male gamete
Write one main difference between asexual and sexual mode of reproduction. Which species is likely to have comparatively better chances of survival – the one reproducing asexually or the one reproducing sexually? Give reason to justify your answer.
Identify A, B, C and D in the given diagram and write their names.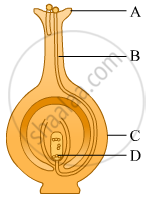
(a) Identify A, B and C in the given diagram and write their functions.
(b) Mention the role of gamete and zygote in sexually reproducing organisms.
Describe an activity to demonstrate phototropism.
Differentiate between self-pollination and cross-pollination.
What is meant by pollination?
Find an odd one out.
Write the functions of sepals
Draw a neat and labelled diagram.
Double fertilization in angiosperms
Identify the parts A, B, C, and D?
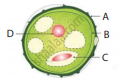
In which part of the flower germination of pollen grains takes place?
Where does the endothecium layer of anther lobes is present?
Sperm and egg nuclei fuse due to ______.
Length of pollen tube depends on the distance between ______
Which among the following statements are true for unisexual flowers?
- They possess both stamen and pistil
- They possess either stamen or pistil
- They exhibit cross pollination
- Unisexual flowers possessing only stamens cannot produce fruits
Which among the following statements are true for sexual reproduction in flowering plants?
- It requires two types of gametes
- Fertilisation is a compulsory event
- It always results in formation of zygote
- Offspring formed are clones
Double fertilization is exhibited by ______
Double fertilization is essential for formation of ______.
Sexual maturation of reproductive tissues and organs are necessary link for reproduction. Elucidate.
What is puberty?
- Assertion: Primary endosperm nucleus is diploid.
- Reason: It is the product of double fertilisation.
