Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State Charles's law.
Solution
Charles's Law
At constant pressure, the volume of a given mass of a dry gas increases or decreases by 1/273rd of its original volume at 0°C for each degree centigrade rise or fall in temperature.
V ∝ T (at constant pressure)
At temperature T1 (K) and volume V1 (cm3):
`"V"_1 ∝ "T"_1 "or" "V"_1/"T"_1 = "K"` = constant...(i)
At temperature T2 (K) and volume V2 (cm3):
`"V"_2 ∝ "T"_2 "or" "V"_2/"T"_2 = "K"` = constant….(ii)
From (i) and (ii),
`"V"_1/"T"_1 = "V"_2/"T"_2` = constant
For Temperature = Conversion from Celsius to Kelvin
1 K = °C + 273
Example:
20°C = 20 + 273 = 293 K
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State the law which is represented by the following graph:
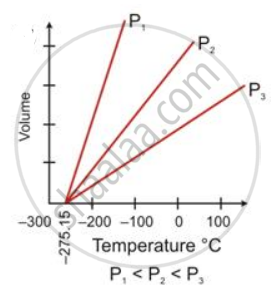
State the following:
Ice point in absolute temperature
What will be the minimum pressure required to compress 500 dm3 of air at 1 bar to 200 dm3 temperature remaining constant?
2500 cm3 of hydrogen is taken at STP. The pressure of this gas is further increased by two and a half times (temperature remaining constant). What volume will hydrogen occupy now?
An LPG cylinder can withstand a pressure of 14.9 atmospheres. The pressure gauge of the cylinder indicates 12 atmospheres at 27°C. Because of a sudden fire in the building, the temperature rises. At what temperature will the cylinder explode?
A certain mass of gas occupied 850 ml at a pressure of 760 mm of Hg. On increasing the pressure it was found that the volume of the gas was 75% of its initial value. Assuming constant temperature, find the final pressure of the gas?
At a given temperature the pressure of a gas reduces to 75% of its initial value and the volume increases by 40% of its initial value. Find this temperature if the initial temperature was -10°C.
Fill in the blank with the correct word, from the words in option:
At -273°C the volume of a gas is theoretically ______.
According to Charles’s law, at constant pressure, the temperature is inversely proportional to volume.
The following question refers to one mole of chlorine gas.
What volume will it occupy at 273°C?
