Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State the role of pancreatic juice in digestion of proteins.
Solution 1
Pancreatic juice contains a variety of inactive enzymes such as trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, and carboxypeptidases. These enzymes play an important role in the digestion of proteins.
Physiology of protein-digestion
The enzyme enterokinase is secreted by the intestinal mucosa. It activates trypsinogen into trypsin.
Trypsinogen  Trypsin + Inactive peptide
Trypsin + Inactive peptide
Trypsin then activates the other enzymes of pancreatic juice such as chymotrypsinogen and carboxypeptidase.
Chymotrypsinogen is a milk-coagulating enzyme that converts proteins into peptides.
Chymotrypsinogen  Chymotrypsin
Chymotrypsin
(Inactive) (Active)
Proteins  Peptides
Peptides
Carboxypeptidase acts on the carboxyl end of the peptide chain and helps release the last amino acids. Hence, it helps in the digestion of proteins.
Peptides 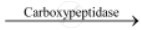 Smaller peptide chain + Amino acids
Smaller peptide chain + Amino acids
Thus, in short, we can say that the partially-hydrolysed proteins present in the chyme are acted upon by various proteolytic enzymes of the pancreatic juice for their complete digestion.
Proteins, peptones 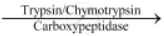 Dipeptides and proteases
Dipeptides and proteases
Solution 2
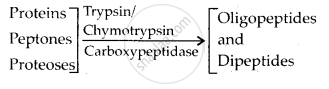
The pancreatic juice contains inactive enzymes – trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, procarboxypeptidases. Trypsinogen is acti¬vated by an enzyme enterokinase, (secreted by the intestinal mucosa) into active trypsin, which in turn activates the other enzymes of the pancreatic juice. Proteins, proteoses and peptones (partially hydrolysed proteins) in the chyme reaching the intestine are acted upon by these proteolytic enzymes of pancreatic juice.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What are the functions of liver?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the small intestine?
Parotid salivary glands occur ______.
Sphincter of oddi is present at ______.
Hepato-pancreatic duct opens into the duodenum and carries ______.
Liver is the largest gland and is associated with various functions. Choose which is not correct from the following.
Does gall bladder make bile?
What is the role of gall bladder? What may happen if it stops functioning or is removed?
What are the various enzymatic types of glandular secretions in our gut helping digestion of food? What is the nature of end products obtained after complete digestion of food?
Discuss the role of hepatic – pancreatic complex in digestion of carbohydrate, protein and fat components of food.
