Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State the rule to determine the direction of a force experienced by a current-carrying straight conductor placed in a magnetic field which is perpendicular to it.
Solution
Fleming's Left-Hand Rule, also known as the Motor Rule, states that the thumb, first finger, and middle finger of the left hand should all be extended such that they are perpendicular to one another. The thumb indicates the direction of the conductor's motion (i.e., the direction of force acting on the conductor) if the first (fore) finger points in the direction of the magnetic field, the middle finger points in the direction of current, and so on.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Which of the following property of a proton can change while it moves freely in a magnetic field? (There may be more than one correct answer.)
Which of the following property of a proton can change while it moves freely in a magnetic field? (There may be more than one correct answer.)
State Fleming's left hand rule.
Name any two factors on which the strength of magnetic field produced by a current-carrying solenoid depends. How does it depend on these factors?
The magnetic field lines in the middle of the current-carrying solenoid are?
(a) circles
(b) spirals
(c) parallel to the axis of the tube
(d) perpendicular to the axis of the tube
A current-carrying straight wire is held in exactly vertical position. If the current passes through this wire in the vertically upward direction, what is the direction of magnetic field produced by it? Name the rule used to find the direction of magnetic field.
When is the force experienced by a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field largest?
For Fleming's left-hand rule, write down the three things that are 90° to each other, and next to each one write down the finger or thumb that represents it.
State Fleming's left-hand rule. Explain it with the help of labelled diagrams.
A horizontal wire carries a current as shown in Figure below between magnetic poles N and S:

Is the direction of the force on the wire due to the magnet:
(a) in the direction the current
(b) vertically downwards
(c) opposite to the current direction
(d) vertically upwards
Two coils A and B of insulated wire are kept close to each other. Coil A is connected to a galvanometer while coil B is connected to a battery through a key. What would happen if:
the current is stopped by removing the plug from the key?
Explain your answer mentioning the name of the phenomenon involved.
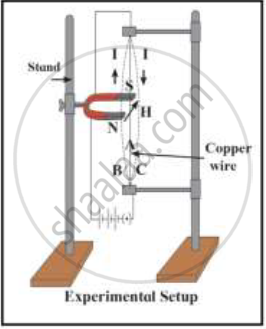
i) Which principle is explained in this figure?
ii) Which rule is used to find out the direction of a force in this principle?
iii) In which machine this principle is used? Draw a diagram showing working of that machine
State two ways to increase the speed of rotation of a D.C. motor.
A current-carrying conductor is held in an exactly vertical direction. In order to produce a clockwise magnetic field around the conductor, the current should be passed in the conductor:
A current flows in a wire running between the S and N poles of a magnet lying horizontally as shown in the figure below:
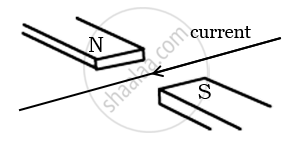
The force on the wire due to the magnet is directed ____________.
The direction of force on a current carrying conductor in a magnetic field is given by ____________.
Observe the given figure of Fleming's Left Hand Rule and write the labels of 'A' and 'B':

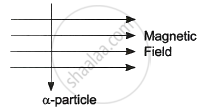
An alpha particle enters a uniform magnetic field as shown. The direction of force experienced by the alpha particle is ______.
Two LED bulbs of 10W and 5W are connected in series. If the current flowing through 5W bulb is 0.005A, the current flowing through 10W bulb is ______.
|
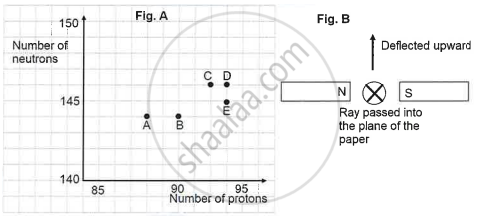
The graph (fig A) illustrates the correlation between the number of protons (x-axis) and the number of neutrons (y-axis) for elements A, B, C, D, and E in the periodic table. These elements are denoted by the letters rather than their conventional symbols. When the element C, depicted in the graph, undergoes radioactive decay, it releases radioactive rays. When these rays are directed into the plane of the paper in the presence of a magnetic field, as indicated in the fig B, they experience deflection, causing them to move upwards.
|
Name the law used to identify the radioactive radiation emitted by the element.