Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Suggest a suitable physical situation for the following graph:
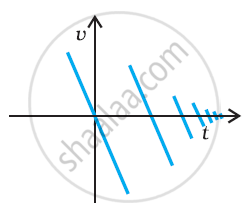
Solution
The (u-t) graph indicates that with time, the velocity repeatedly reverses direction while experiencing a decrease in magnitude after each reversal. This coulde represent a physical situation where a ball, initially thrown upwards and then subject to free fall, impacts the ground, rebounding each time with diminishing speed following each contact with the ground.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A jet airplane travelling at the speed of 500 km h–1 ejects its products of combustion at the speed of 1500 km h–1 relative to the jet plane. What is the speed of the latter with respect to an observer on ground?
A man walks on a straight road from his home to a market 2.5 km away with a speed of 5 km h –1. Finding the market closed, he instantly turns and walks back home with a speed of 7.5 km h–1.
- What is the magnitude of average velocity, and
- average speed of the man over the interval of time
- 0 to 30 min,
- 0 to 50 min,
- 0 to 40 min?
[Note: You will appreciate from this exercise why it is better to define average speed as total path length divided by time, and not as magnitude of average velocity. You would not like to tell the tired man on his return home that his average speed was zero!]
In Exercise, we have carefully distinguished between average speed and magnitude of average velocity. No such distinction is necessary when we consider instantaneous speed and magnitude of velocity. The instantaneous speed is always equal to the magnitude of instantaneous velocity. Why?
In the following figure shows the graph of the x-coordinate of a particle going along the X-axis as a function of time. Find instantaneous velocity at 2, 5, 9 and 12s.

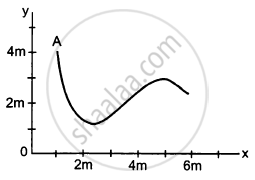
Figure A particle starts from a point A and travels along the solid curve shown in the following figure. Find approximately the position B of the particle such that the average velocity between the position A and B has the same direction as the instantaneous velocity at B.
Two cars are moving with speeds of 40 km/hr due North and 40 km/hr due South respectively. Do they have the same velocity?
In one dimensional motion, instantaneous speed v satisfies 0 ≤ v < v0.
The displacement of a particle is given by x = (t – 2)2 where x is in metres and t in seconds. The distance covered by the particle in first 4 seconds is ______.
A particle executes the motion described by x(t) = x0 (1 − e − γt); t ≥ 0, x0 > 0. Where does the particle start and with what velocity?
A monkey climbs up a slippery pole for 3 seconds and subsequently slips for 3 seconds. Its velocity at time t is given by v(t) = 2t (3 – t); 0 < t < 3 and v(t) = – (t – 3)(6 – t) for 3 < t < 6 s in m/s. It repeats this cycle till it reaches the height of 20 m.
- At what time is its velocity maximum?
- At what time is its average velocity maximum?
- At what time is its acceleration maximum in magnitude?
- How many cycles (counting fractions) are required to reach the top?
