Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The angle of elevation of the top of a tower from a point A due south of the tower is α and from B due east of the tower is β. If AB = d, show that the height of the tower is
`\frac{d}{\sqrt{\cot ^{2}\alpha +\cot^{2}\beta `
Sum
Solution
Let OP be the tower and let A and B be two points due south and east respectively of the tower such that ∠OAP = αand ∠OBP = β.
Let OP = h. In ∆OAP, we have
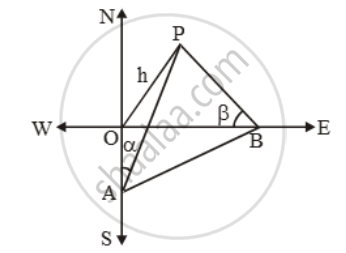
`\tan \alpha =\frac{h}{OA}`
⇒ OA = h cot α ….(i)
In ∆OBP, we have
`\tan \beta =\frac{h}{OB}`
⇒ OB = h cot β. ….(ii)
Since OAB is a right angled triangle. Therefore,
`AB^2 = OA^2 + OB^2`
`⇒ d^2 = h^2 cot^2 α + h^2 cot^2 β`
`\Rightarrow h=\frac{d}{\sqrt{\cot ^{2}\alpha +\cot ^{2}\beta )`
[Using (i) and (ii)]
shaalaa.com
Is there an error in this question or solution?
