Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Given below are the diagrams of a certain structure in plants in two conditions.

(i) Name the structure shown.
(ii) Name the parts numbered 1-5.
(iii) What is the most apparent difference between A and B in the structure shown?
(iv) Describe the mechanism which brings about the change in the structure depicted in A and B.
Solution
(i) Stomata surrounded by epidermal cells.
(ii)
- Chloroplast,
- The inner wall of guard cells,
- Nucleus,
- Guard cells,
- Stoma.
(iii) The stoma is open in A and is almost closed in B.
(iv) The opening and dosing mechanism of stomata is regulated by the amount of water and solutes present in the guard cells. The guard cells have a thick inner wall facing the opening and a thin outer wall on the opposite side; their cytoplasm contains chloroplasts. During the day guard cells begin photosynthesis and the sugar produced during the process increases the osmotic pressure which draws in water from the adjoining cells. Hence, the guard cells become turgid and bulge outward due to their thin outer wall, thus widening the stomatal opening lying in between (A). As the stomata open, the diffusion of gases in and out begins to fulfilling the need for photosynthesis and for allowing transpiration. If for any reason the water content of the leaf is falling short, the guard cells fail to remain turgid, they turn flaccid or lose turgidity, thereby closing the stomatal opening (B) and the transpiration stops.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name the following:
Any two parts of a leaf which allow transpiration.
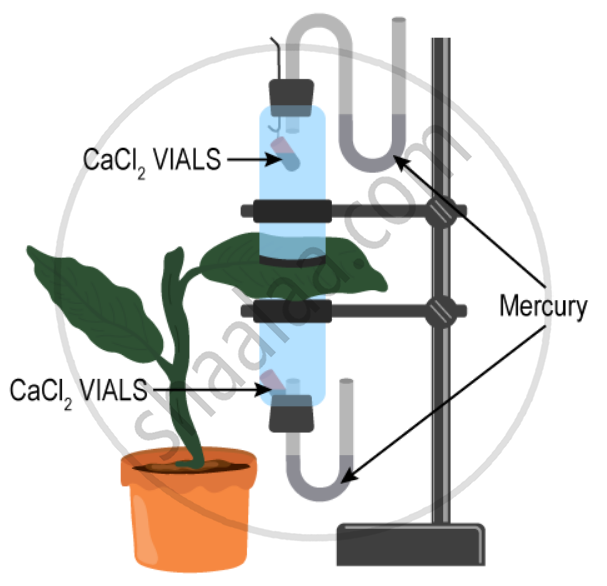
The apparatus shown in the following diagram is Garreau’s potometer designed to demonstrate unequal transpiration from the two surfaces of a dorsiventral leaf. Before keeping the leaf in between the cups, anhydrous calcium chloride (CaCl2) contained in two small vials were weighed and placed in both the cups. The ends of the cups were closed with corks through which two mercury manometers were connected. After few hours, CaCl2 vials were taken out and weighed again.
What do you mean by transpiration?
Where are stomata generally found?
The figure below represents the vertical section of a leaf:

(i) Name the parts labeled 1 to 5.
(ii) What do the two arrows (dotted and solid) indicate in the day time and at night?
(iii) Could you add one more arrow in the figure? If yes, what for?
(iv) How many leaf veins have been shown in this section?
Choose the Odd One Out
Write a short note on lenticular transpiration.
The upper layer of mesophyll in a leaf consists of elongated ground tissue called ______.
