Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The emf induced across the ends of a conductor due to its motion in a magnetic field is called motional emf. It is produced due to magnetic Lorentz force acting on the free electrons of the conductor. For a circuit shown in the figure, if a conductor of length l moves with velocity v in a magnetic field B perpendicular to both its length and the direction of the magnetic field, then all the induced parameters are possible in the circuit.
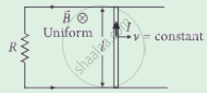
A 0.1 m long conductor carrying a current of 50 A is held perpendicular to a magnetic field of 1.25 mT. The mechanical power required to move the conductor with a speed of 1 ms-1 is ______.
Options
62.5 mW
625 mW
6.25 mW
12.5 mW
Solution
A 0.1 m long conductor carrying a current of 50 A is held perpendicular to a magnetic field of 1.25 mT. The mechanical power required to move the conductor with a speed of 1 ms-1 is 6.25 mW.
Explanation:
Here, l = 0.1 m, v = 1 ms-1
I = 50 A, B = 1.25 mT = 1.25 × 10-3 T
The induced emf is, ε = Blv
The mechanical power is
P = εI = BlvI = 1.25 × 10-3 × 0.1 × 1 × 50
= 6.25 × 10-3 W
= 6.25 mW
