Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The following diagram shows a part of the periodic table containing first three periods in which five elements have been represented by the letters a, b, c, d and e (which are not their chemical symbols):
-
1 18 a 2 13 14 15 16 17 b c d e
(i) Select the letter which represents an alkali metal.
(ii) Select the letter which represents a nobles gas.
(iii) Select the letter which represents a halogen.
(iv) What type of bond is formed between a and e?
(v) What type of bond is formed between d and e?
Solution
(i) The letter 'd' represents an alkali metal. This is because group 1 elements of the periodic table, except hydrogen, are all alkali metals having 1 valence electron.
(ii) The letter 'c' represents a noble gas. All the group 18 elements are noble gases or inert gases whose valence shells are completely filled with electrons.
(iii) The letter 'e' represents a halogen. Group 17 elements are known as halogens and they have 7 valence electrons.
(iv) A covalent bond is formed between 'a' and 'e'. 'a', the top most element represents hydrogen which is the only non-metal in group 1. Therefore, when a non-metal 'a' forms a compound with another non-metal 'e', sharing of electrons takes place resulting in the formation of a covalent bond.
(v) An ionic bond is formed between 'd' and 'e'. When a metal reacts with a non-metal, a transfer of electrons takes place from the metal to the non-metal and results in the formation of an ionic bond.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An element X is in group 2 of the periodic table what will be the formula of its oxide?
An element Y is in second period and group 16 of the periodic table:
(i) Is it a metal or non-metal?
(ii) What is the number of valence electrons in its atom?
(iii) What is its valency?
(iv) What is the name of the element?
(v) What will be the formula of the compound formed by Y with sodium?
Atoms of eight elements A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H have the same number of electron shells but different number of electrons in their outermost shells. It was found that elements A and G combine to form an ionic compound. This ionic compound is added in a small amount to almost all vegetables and dishes during cooking. Oxides of elements A and B are basis in nature while those of elements E and F acidic. The oxide of element D is, however, almost neutral. Based on the above information, answer the following questions:
(a) To which group or period of the periodic table do these elements belong?
(b) What would be the nature of compound formed by a combination of elements B and F?
(c) Which two of these elements could definitely be metals?
(d) Which one of the eight elements is most likely to be found in gaseous state at room temperature?
(e) If the number of electrons in the outermost shell of elements C and G be 3 and 7 respectively, write formula of the compound formed by the combination of C and G.
Answer the following question.
Write the name, symbol, and electronic configuration of an element X whose atomic number is 11.
Among the given species A–, A+, and A, the smallest one in size is ______.
In which group are inert elements placed?
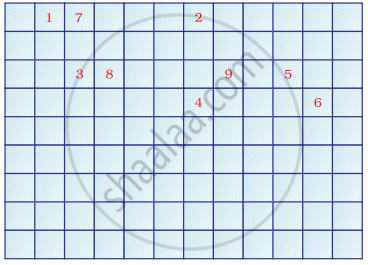
Complete the following cross word puzzle
Across:
(1) An element with atomic number 12.
(3) Metal used in making cans and member of Group 14.
(4) A lustrous non-metal which has 7 electrons in its outermost shell.
Down:
(2) Highly reactive and soft metal which imparts yellow colour when subjected to flame and is kept in kerosene.
(5) The first element of second Period
(6) An element which is used in making fluorescent bulbs and is second member of Group 18 in the Modern Periodic Table
(7) A radioactive element which is the last member of halogen family.
(8) Metal which is an important constituent of steel and forms rust when exposed to moist air.
(9) The first metalloid in Modern Periodic Table whose fibres are used in making bullet-proof vests
Which of the following metals have low melting and boiling point?
Complete the following triads by inserting the missing elements.
Cl, ______, I
How are elements grouped into various families in the periodic table?
