Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The following table shows the current in Amperes and potential differences in Volts.
- Find the average resistance.
- What will be the nature of the graph between the current and potential difference? (Do not draw a graph.)
- Which law will the graph prove? Explain the law.
| V (volts) | I (amp) |
| 4 | 9 |
| 5 | 11.25 |
| 6 | 13.5 |
Solution
From the following table,
V1 = 4V, V2 = 5V, V3 = 6V
I1 = 9 A, I2 = 11.25 A, I3 = 13.5 A
`"R"_1 = "V"_1/"I"_1 = 4/9 = 0.44 Omega`
`"R"_2 = "V"_2/"I"_2 = 5/11.25 = 0.44 Omega`
`"R"_3 = "V"_3/"I"_3 = 6/13.5 = 0.44 Omega`
| V (Volt) | I (Ampere) | R(Ω) = `bb"V"/bb"I"` |
| 4 | 9 | 0.44 |
| 5 | 11.25 | 0.44 |
| 6 | 13.5 | 0.44 |
a. Average resistance (R) = `("R"_1 + "R"_2 + "R"_3)/3`
= `(0.44 + 0.44 + 0.44)/3`
= `1.32/3 = 0.44`
∴ Average resistance (R) = 0.44 Ω
b. A straight line will pass through the origin (0, 0) on the graph between current and potential difference.
c. Here `"V"_1/"I"_1 = "V"_2/"I"_2 = "V"_3/"I"_3` i.e. Ohm's law is clear from I ∝ V.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What actually travels through the wires when you switch on a light?
How many microamperes are there in 1 ampere?
A Radio Set Draws a Current of 0.36 a for 15 Minutes. Calculate the Amount of Electric Charge that Flows Through the Circuit.
A p.d. of 6 V is applied to two resistors of 3 Ω and 6 Ω connected in parallel. Calculate:
(a) the combined resistance
(b) the current flowing in the main circuit
(c) the current flowing in the 3 Ω resistor.
In which of the following cases more electrical energy is consumed per hour?
(i) A current of 1 ampere passed through a resistance of 300 ohms.
(ii) A current of 2 amperes passed through a resistance of 100 ohms.
For a heater rated at 4 kW and 220 V, calculate:
(a) the current,
(b) the resistance of the heater,
(c) the energy consumed in 2 hours, and
(d) the cost if 1 kWh is priced at Rs 4.60.
A switch must be connected in:
(a) Live wire (b) neutral wire
(c) earth wire (d) either earth or neutral wire
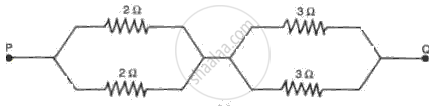
Find the effective resistance in the following circuit diagrams (Fig.):
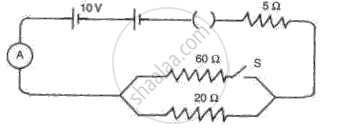
In the circuit shown in fig. 6, find the reading of the ammeter A when the switch S is
(a) Opened.
(b) Closed.
What is the purpose of fuse in an electrical circuit?
An electric bulb is rated 250 W, 230 V.
- the energy consumed in one hour, and
- the time in which the bulb will consume 1.0 kWh energy when connected to 230 V mains.
An electrical gadget can give an electric shock to its user under certain circumstances. Mention any two of these circumstances.
Water : pipe :: Electric current : ______.
Match the following:
| 1. | 1 mA | a. | series |
| 2. | 1 pA | b. | ohmmeter |
| 3. | Ammeter | c. | 10-6 ampere |
| 4. | Electrical resistivity | d. | 10-3 ampere |
A charge of 400C flows through a conductor for 13 minutes and 20 seconds. Find the magnitude of the current flowing through the conductor.
1020 electrons, each having a charge of 1.6 x 10-19 C, flows in a circuit V is 0.1s. What is the current in ampere?
Define the following:
Conventional current and electron current
