Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
|
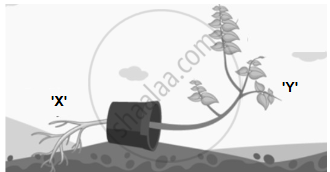
The growth movements of plant parts in which the direction of the stimulus determines the direction of the response are known as tropic movements or tropism. Plants also have non-directional movements, which may not be growth-dependent.
|
- Name the movement which causes ‘X’ and ‘Y’ to grow downwards and upwards respectively. (1)
- Write the name of a hormone that plays a major role in
- falling of leaves.
- rapid cell division. (1)
-
- Leaves of the sensitive plant move very quickly in response to ‘touch’. How is this stimulus of touch communicated and explain how the movement takes place? (2)
OR - Name the plant hormone which is synthesized at the shoot tip. How does this hormone help the plant to bend towards light? (2)
- Leaves of the sensitive plant move very quickly in response to ‘touch’. How is this stimulus of touch communicated and explain how the movement takes place? (2)
Case Study
Solution
I.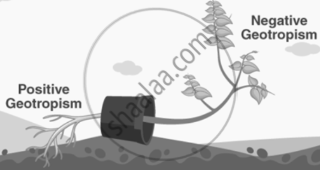
II.
- Abscisic acid (ABA)
- Cytokini
III.
-
- The leaves of Mimosa pudica fold in response to touch due to Thigmonastic (Seismonastic) Movement.
- The stimulus is communicated by an electrochemical signal, leading to changes in turgor pressure in specialized cells called pulvini.
- When touched, water moves out of pulvini cells, causing them to collapse, leading to the folding of leaves.
OR
-
- Auxin is the hormone synthesized at the shoot tip.
- Auxin accumulates on the shaded side of the shoot. This promotes cell elongation on that side, causing the shoot to bend towards the light. This response is called Phototropism (Positive Phototropism in shoots).
shaalaa.com
Is there an error in this question or solution?