Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The growth of a pollen tube towards the ovule caused by a sugary substance as stimulus is an example of :
(a) phototropism
(b) chlorotropism
(c) gravitropism
(d) chemotropism
Solution
(d) chemotropism
The growth of pollen tubes towards the ovule caused by a sugary substance is an example of chemotropism.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give the scientific terms used to represent the Winding of tendril around a support.
Give one example of a plant part which is positively phototropic but negatively geotropic.
The plant hormone which triggers the fall of mature leaves and fruits from the plant body is:
Which of the following terms denotes the movement of the root of a plant towards moisture in the soil?
(a) thigmotropism
(b) chemotropism
(c) hydrotropism
(d) geotropism
What are tropic movements? Briefly explain various types of tropic movements in plants.
Differentiate phototropism from photonasty.
Chlorophyll differs from hemoglobin by the presence of its central molecule ______.
Name the following:
The tropic movement of plant parts in response to chemicals.
Study the diagrams given below and answer the following questions:
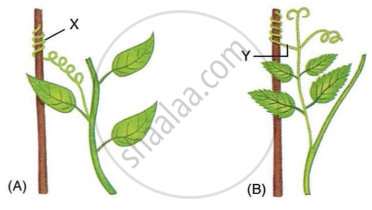
- Name the structures shown as X and Y in the figures (A) and (B), respectively.
- Write the functions performed by the structures X and Y.
- Name the phenomenon depicted and define it.
- How do the structures X and Y differ from each other?
- Give examples of the plants which show the said phenomenon.
Given below are the figures showing some kinds of tropic movements in plants. Study the same and answer the following questions:
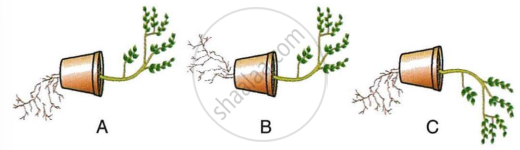
- Which one of these figures is correct? Give reason in support of your answer.
- Name the kinds of movements shown by the root system and shoot system. Define each.
- What are the two stimuli which affect root system and shoot system positively? Name them.
- Which of the following stimuli affects the growth of the root strongly?
- Gravity
- Water
- Draw a neat and labelled diagram of the longitudinal section of a pistil showing chemotropism in an angiospermic plant.
