Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The teachers of Geeta’s school took the students on a study trip to a power generating station, located nearly 200 km away from the city. The teacher explained that electrical energy is transmitted over such a long distance to their city, in the form of alternating current (ac) raised to a high voltage. At the receiving end in the city, the voltage is reduced to operate the devices. As a result, the power loss is reduced. Geeta listened to the teacher and asked questions about how the ac is converted to a higher or lower voltage.
1) Name the device used to change the alternating voltage to a higher or lower value. State one cause for power dissipation in this device.
2) Explain with an example, how power loss is reduced if the energy is transmitted over long distances as an alternating current rather than a direct current.
3) Write two values each shown by the teachers and Geeta.
Solution
1) The transformer is a device used for changing the alternating voltage to a higher or lower value. Formation of eddy currents in the iron core of the transformer is one of the causes of power dissipation in this device.
2) In the long-distance transmission of energy through transmission lines, the power loss is mainly due to resistive loss. Now, this resistive loss is proportional to the square of current flowing through the lines i.e
`H prop I^2`
So, to minimise this loss, we need to minimise the current flowing in the wire. In case of dc, if we decrease the current flowing in the wire, though the power losses will decrease but simultaneous power received at the receiving station will also decrease. So, to achieve the required amount of power at the receiving station, we transmit the ac signal by stepping up the voltage with the lower value of current as ac gives the flexibility of stepping up or down the voltage. In this way, the power losses are reduced while maintaining the required amount of power at the receiving station.
3)
Two values shown by the teachers are:
- Believer of giving practical knowledge
- Good explainer
Two values shown by Geeta are:
- Curiosity of learning
- Good listener
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name two factors on which the magnitude of an induced e.m.f. in the secondary coil depends.
Why is the core of a transformer laminated?
The following diagram in Fig.10.42 shows a coil of several turns of copper wire connected to a sensitive centre zero galvanometer G near a magnet NS. The coil is free to move in the direction shown in the diagram.
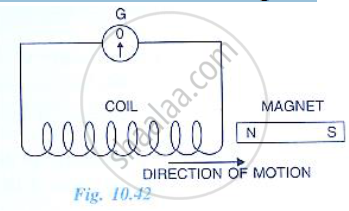
(i) Describe the observation if the coil is rapidly moved.
(ii) How would the observation be altered if (a) the coil has twice as many turns (b the coil was made to move three times as fast?
Mention the two characteristic properties of the material suitable for making core of a transformer.
State the underlying principle of a transformer. How is the large scale transmission of electric energy over long distances done with the use of transformers?
What is the ideal transformer?
Why is the core of a transformer made of soft iron?
The power supply to the primary coil of a transformer is 200 W. Find
(i) Current in primary coil if the e.m.f. supply to it is equal to 220V.
(ii) The number of turns in the primary coil is equal to 80 and that in secondary is 800. What is the transformation ratio?
(iii) Name the type of transformer.
(iv) What will be the output voltage?
(v) What is the current in the secondary coil for an ideal transformer?
(vi) What is the output power?
(vii) Is output and input power equal?
(viii) Compare the current flowing in a secondary coil and in a primary coil.
1 MW power is to be delivered from a power station to a town 10 km away. One uses a pair of Cu wires of radius 0.5 cm for this purpose. Calculate the fraction of ohmic losses to power transmitted if
- power is transmitted at 220 V. Comment on the feasibility of doing this.
- a step-up transformer is used to boost the voltage to 11000 V, power transmitted, then a step-down transfomer is used to bring voltage to 220 V. (ρCu = 1.7 × 10–8 SI unit)
Mention two main sources of power loss in real transformers.
