Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The top part A of the flask-shaped reproductive organ X in the flower of a plant secrets a surgery substance into its lower part B which goes towards the bottom part C of the flask-shaped organ. When a tiny grain D coming from the top part E of another reproductive organ Y i the flower falls on part A, it grows a long tube F through the organ X i response to the sugary substance and reaches the bottom part C of flask-shaped organ to carry out fertilisation.
(a) Name parts (i) organ X, and (ii) organ Y, inside the flower?
(b) Name parts (i) A (ii) B, and (iii) C, of flask-shaped organ.
(c) Name (i) grain D, and (ii) part E of organ Y.
(d) Name the tube F.
(e) What is the phenomenon of growing a long tube in response to sugary substance in the process of fertilisation in a flower known as?
Solution
(a) (i) X is the carpel and (ii) Y is the stamen.
(b) (i) A is the stigma, (ii) B is the style and (iii) C is the ovary of the flask-shaped organ.
(c) (i) D is the pollen and (ii) E is the anther.
(d) F is the pollen tube.
(e) The phenomenon of growing a long tube in response to a sugary substance in the process of fertilisation in a flower is known as chemotropism.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Plant roots grow downward in response to ______.
A potted plant is kept horizontally for a considerable time. The three positions of the parts A and B of the potted plant are shown in the following figures:
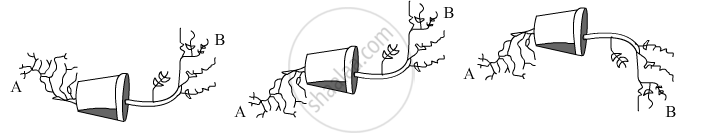
- Which figure shows the correct position taken by the parts A and B of the plant?
- What type of phenomenon is exhibited by the figure chosen in (a) above?
Which of the following terms denotes the movement of the root of a plant towards moisture in the soil?
(a) thigmotropism
(b) chemotropism
(c) hydrotropism
(d) geotropism
The climbing organs of plants like tendrils grow towards any support which they happen to touch and wind around the support. This is an example of :
(a) chemotropism
(b) nastic movement
(c) thigmotropism
(d) geotropism
The chemical substance P is made and secreted by the meristematic tissue at the tip of stem (or shoot) of a plant. The chemical substance P is responsible for a phenomenon Q in plants in which the stem bends towards a source of light. The same chemical substance P has an opposite effect on the root of a plant. It causes the root of a plant to bend away from the source of light in a process called R.
(a) What is the chemical substance P?
(b) State whether P prefers to remains in the sunlit side of a stem or in shade.
(c) What is the effect of substance P on the rate of growth of (i) a root, and (ii) a stem?
(d) What is the name of process (i) Q, and (ii) R?
(e) What is the general name of chemical substances like P? Name another substance which belongs to this class of chemical substances.
The bending of root of a plant in response to water is called ______.
A growing seedling is kept in the dark room. A burning candle is placed near it for a few days. The tip part of the seedling bends towards the burning candle. This is an example of ______.
Assertion: Plants do have a nervous system for control and coordination.
Reason: Plants use electrochemical means to convey information from cell to cell.
The height of a plant is regulated by ______.
Growth of root towards water is ______.
