Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The yellow colour has a greater luminous efficiency as compared to the other colours. Can we increase the illuminating power of a white light source by putting a yellow plastic paper around this source?
Solution
No, we cannot increase the illuminating power of any white light source by wrapping a yellow plastic around them.
White light emits power in all wavelengths of visible radiation, and the yellow plastic will block all the other wavelengths other than the yellow one. This means that it will allow only a small amount of power, emitted by the white light, in the yellow coloured wavelength and block the rest. Thus, it will decrease the illuminating power of the source.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Why is the luminous efficiency small for a filament bulb as compared to a mercury vapour lamp?
The one parameter that determines the brightness of a light source sensed by an eye is ____________ .
As the wavelength is increased from violet to red, the luminosity ____________ .
A photographic plate is placed directly in front of a small diffused source in the shape of a circular disc. It takes 12s to get a good exposure. If the source is rotated by 60° about one of its diameter, the time needed to get the same exposure will be ___________ .
A point source of light moves in a straight line parallel to a plane table. Consider a small portion of the table directly below the line of movement of the source. The illuminance at this portion varies with its distance r from the source as ___________ .
Figure shows a glowing mercury tube. The intensities at point A, B and C are related as __________ .
A room is illuminated by an extended source. The illuminance at a particular portion of a wall can be increased by
(a) moving the source
(b) rotating the source
(c) bringing some mirrors in proper positions
(d) changing the colour of the source.
Mark the correct options.
(a) The luminous efficiency of a monochromatic source is always greater than that of a white light source of same power.
(b) The luminous efficiency of a monochromatic source of wavelength 555 nm is always greater than that of a white light source of same power.
(c) The illuminating power of a monochromatic source of wavelength 555 nm is always greater than that of a white light source of same power.
(d) The illuminating power of a monochromatic source is always greater than that of a white light source of same power.
Using figure, find the relative luminosity of wavelength (a) 480 nm, (b) 520 nm (c) 580 nm and (d) 600 nm.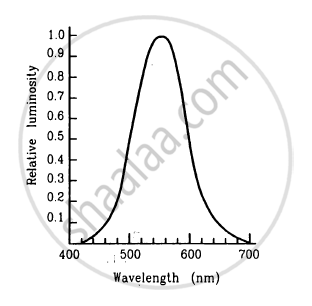
The relative luminosity of wavelength 600 nm is 0.6. Find the radiant flux of 600 nm needed to produce the same brightness sensation as produced by 120 W of radiant flux at 555 nm.
A light source emits monochromatic light of 555 nwavelengthm. The source consumes 100 W of electric power and emits 35 W of radiant flux. Calculate the overall luminous efficiency.
A source emits 31.4 W of radiant flux distributed uniformly in all directions. The luminous efficiency is 60 lumen watt−1. What is the luminous intensity of the source?
A point source emitting 628 lumen of luminous flux uniformly in all directions is placed at the origin. Calculate the illuminance on a small area placed at (1.0 m, 0, 0) in such a way that the normal to the area makes an angle of 37° with the X-axis.
The illuminance of a small area changes from 900 lumen m−2 to 400 lumen m−2 when it is shifted along its normal by 10 cm. Assuming that it is illuminated by a point source placed on the normal, find the distance between the source and the area in the original position.
A point source emitting light uniformly in all directions is placed 60 cm above a table-top. The illuminance at a point on the table-top, directly below the source, is 15 lux. Find the illuminance at a point on the table-top 80 cm away from the first point.
Light from a point source falls on a small area placed perpendicular to the incident light. If the area is rotated about the incident light by an angle of 60°, by what fraction will the illuminance change?
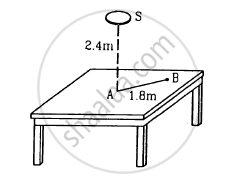
Figure shows a small diffused plane source S placed over a horizontal table-top at a distance of 2.4 m with its plane parallel to the table-top. The illuminance at the point Adirectly below the source is 25 lux. Find the illuminance at a point B of the table at a distance of 1.8 m from A.
An electric lamp and a candle produce equal illuminance at a photometer screen when they are placed at 80 cm and 20 cm from the screen respectively. The lamp is now covered with a thin paper which transmits 49% of the luminous flux. By what distance should the lamp be moved to balance the intensities at the screen again?
Light rays from a point object ______.
