Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
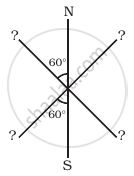
Three identical bar magnets are rivetted together at centre in the same plane as shown in figure. This system is placed at rest in a slowly varying magnetic field. It is found that the system of magnets does not show any motion. The north-south poles of one magnet is shown in the figure. Determine the poles of the remaining two.
Solution
If the net force on the system is zero and net torque on the system is also zero, then the system will be in stable equilibrium. This is possible only when the poles of the remaining two magnets are as shown below.
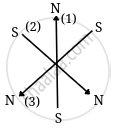
The north pole of magnet (1) is equally attracted by south poles of (2) and (3) magnets placed at equal distance.
Similarly, one pole of any one magnet is attracted by opposite poles of other two magnets so resultant force or moment of each magnet is zero and will not be in motion placed on table.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Consider a magnetic dipole kept in the north to south direction. Let P1, P2, Q1, Q2 be four points at the same distance from the dipole towards north, south, east and west of the dipole respectively. The directions of the magnetic field due to the dipole are the same at
(a) P1 and P2
(b) Q1 and Q2
(c) P1 and Q1
(d) P2 and Q2
A rod, when suspended in a magnetic field, stays in the east-west direction. Can we be sure that the field is in the east-west direction? Can it be in the north-south direction?
Electromagnets are made of soft iron because soft iron has _______________ .
Pick the correct options.
(a) All electrons have magnetic moment.
(b) All protons have magnetic moment.
(c) All nuclei have magnetic moment.
(d) All atoms have magnetic moment.
The susceptibility of annealed iron at saturation is 5500. Find the permeability of annealed iron at saturation.
An a-particle and a proton of the same kinetic energy are in turn allowed to pass through a magnetic field `vec"B"`, acting normal to the direction of motion of the particles. Calculate the ratio of radii of the circular paths described by them.
The magnetism of a magnet is due to ______
The primary origin(s) of magnetism lies in ______.
- atomic currents.
- pauli exclusion principle.
- polar nature of molecules.
- intrinsic spin of electron.
