Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Two cylindrical vessels fitted with pistons A and B of area of cross-section 8 cm2 and 320 cm2 respectively are joined at their bottom by a tube and they are completely filled with water. When a mass of 4 kg is placed on piston A, Find:
- the pressure on piston A,
- the pressure on piston B, and
- the thrust on piston B.
Solution
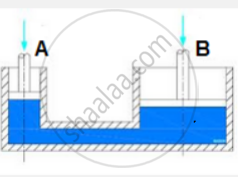
Given that the force applied to the smaller piston A is 4 kg
Area of cross-section of piston A = 8 cm²
Area of cross-section of piston B = 320 cm²
(i) Pressure acting on piston A in the downward direction = `"Thrust"/"Area"`
= `(4 "kg")/(8 "cm"^2)`
∴ Pressure acting on piston A = 0.5 kg cm-2
(ii) According to Pascal's Law
Pressure acting on piston B = Pressure acting on Piston A = 0.5 kg cm-2
(iii) Thrust acting on piston B in the upward direction
= Pressure × Area of B
= 4 kg × `(320 "cm"^2)/(8 "cm"^2)`
∴ Thrust acting on piston B in the upward direction = 160 kgf.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What do you mean by buoyancy?
The density of water is 1.0 g Cm-3. The density of iron is 7.8 × 10″3 g Cm-3. The density of mercury is 13.6 g Cm-3.
Answer the following:
Will a piece of iron float or sink in mercury?
How does the pressure exerted by thrust depend on the area of surface on which it acts? Explain with a suitable example.
Write an expression for the pressure at a point inside a liquid. Explain the meaning of the symbols used.
A small block of wood is completely immersed in (i) water, (ii) glycerine and then released. In each case, What do you observe? Explain the difference in your observation in the two cases.
Prove that the loss in weight of a body when immersed wholly or partially in a liquid is equal to the buoyant force (or upthrust) and this loss is because of the difference in pressure exerted by liquid on the upper and lower surfaces of the submerged part of body.
A beaker contains a liquid of density ‘ρ’ up to height ‘h’ such that ‘PA’ is atmospheric pressure and ‘g’ is the acceleration due to gravity. Answer the following questions:
- What is the pressure on the free surface of the liquid?
- What is the pressure on the base of the beaker?
- What is the lateral pressure at the base on the inner walls of the beaker?
What is meant by up thrust?
The magnitude of buoyant force acting on an object immersed in a liquid depends on ______ of the liquid.
Most buoyant objects are those with relatively ______.
- high volume
- higher mass
- low density
- less viscosity
