Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Use the data in the Table given below to answer the following –
Which material is the best conductor?
Table give below Electrical resistivity of some substances at 20°C
| Electrical resistivity of some substances at 20°C | ||
| − | Material | Resistivity (Ω m) |
| Conductors |
Silver | 1.60 × 10−8 |
| Copper | 1.62 × 10−8 | |
| Aluminium | 2.63 × 10−8 | |
| Tungsten | 5.20 × 10−8 | |
| Nickel | 6.84 × 10−8 | |
| Iron | 10.0 × 10−8 | |
| Chromium | 12.9 × 10−8 | |
| Mercury | 94.0 × 10−8 | |
| Manganese | 1.84 × 10−6 | |
| Alloys |
Constantan (alloy of Cu and Ni) |
49 × 10−6 |
| Manganin (alloy of Cu, Mn and Ni) |
44 × 10−6 | |
| Nichrome (alloy of Ni, Cr, Mn and Fe) |
100 × 10−6 | |
| Insulators | Glass | 1010 − 1014 |
| Hard rubber | 1013 − 1016 | |
| Ebonite | 1015 − 1017 | |
| Diamond | 1012 − 1013 | |
| Paper (dry) | 1012 | |
Solution 1
It can be observed from the Table given in the question that the resistivity of silver is the lowest among the listed materials. Hence, it is the best conductor.
Solution 2
Silver is the best conductor as its resistivity (ρ) is the least, i.e., 1.60 × 10-8 Ωm.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Use the data in the Table given below to answer the following –
Which among iron and mercury is a better conductor?
Table give below Electrical resistivity of some substances at 20°C
| Electrical resistivity of some substances at 20°C | ||
| − | Material | Resistivity (Ω m) |
| Conductors |
Silver | 1.60 × 10−8 |
| Copper | 1.62 × 10−8 | |
| Aluminium | 2.63 × 10−8 | |
| Tungsten | 5.20 × 10−8 | |
| Nickel | 6.84 × 10−8 | |
| Iron | 10.0 × 10−8 | |
| Chromium | 12.9 × 10−8 | |
| Mercury | 94.0 × 10−8 | |
| Manganese | 1.84 × 10−6 | |
| Alloys |
Constantan (alloy of Cu and Ni) |
49 × 10−6 |
| Manganin (alloy of Cu, Mn and Ni) |
44 × 10−6 | |
| Nichrome (alloy of Ni, Cr, Mn and Fe) |
100 × 10−6 | |
| Insulators | Glass | 1010 − 1014 |
| Hard rubber | 1013 − 1016 | |
| Ebonite | 1015 − 1017 | |
| Diamond | 1012 − 1013 | |
| Paper (dry) | 1012 | |
What is (a) the highest, (b) the lowest total resistance that can be secured by combinations of four coils of resistance 4 Ω, 8 Ω, 12 Ω, 24 Ω?
A copper wire has diameter 0.5 mm and resistivity of 1.6 × 10−8Ω m. What will be the length of this wire to make its resistance 10 Ω? How much does the resistance change if the diameter is doubled?
Why are copper and aluminium wires usually employed for electricity transmission?
Why are alloys commonly used in electrical heating devices? Give reason.
Which of the following are conductors and which are insulators?
Sulphur, Silver, Copper, Cotton, Aluminium, Air, Nichrome, Graphite, Paper, porcelain, Mercury, Mica, Bakelite, Polythene, Manganin.
What is the general name of the substances having infinitely high electrical resistance?
What happens to the resistance as the conductor is made thinner?
How does the resistance of a conductor depend on:
temperature of the conductor?
What would be the effect on the resistance of a metal wire of:
increasing its diameter?
What would be the effect on the resistance of a metal wire of:
increasing its temperature?
Calculate the area of cross-section of a wire if its length is 1.0 m, its resistance is 23 Ω and the resistivity of the material of the wire is 1.84 × 10−6 Ω m.
The figure blow shows a variable resistor in a dimmer switch.
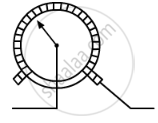
How would you turn the switch to make the lights: (a) brighter, and (b) dimmer? Explain your answer.
Write the relation between resistance and electrical resistivity of the material of a conductor in the shape of a cylinder of length `'l'` and area of cross-section `'A'` . Hence derive the S.I. unit of electrical resistivity.
A cylindrical conductor of length l and uniform area of cross-section A has resistance R. Another conductor of length 2l and resistance R of the same material has an area of cross-section:
How will you infer with the help of an experiment that the same current flows through every part of the circuit containing three resistances in series connected to a battery?
The resistance of a wire of 0.01 cm radius is 10 Ω. If the resistivity of the wire is 50 × 10-8 Ω, find the length of this wire.
