Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Water in lakes and ponds do not freeze at once in cold countries. Give a reason is support of your answer.
Solution
The specific latent heat of fusion of ice is sufficiently high (=336 J g-1), and so to freeze water, a large quantity of heat has to be withdrawn. Hence, it freezes slowly and thus keeps the surroundings moderate.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The temperature of 170 g of water at 50°C is lowered to 5°C by adding a certain amount of ice to it. Find the mass of ice added.
Given: Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg-1 °C-1 and specific latent heat of ice = 336000 J kg-1.
Water property of water makes it an effective coolant?
A calorimeter has mass 100 g and specific heat 0.1 kcal/ kg °C. It contains 250 gm of liquid at 30°C having specific heat of 0.4 kcal/kg °C. If we drop a piece of ice of mass 10 g at 0°C, What will be the temperature of the mixture?
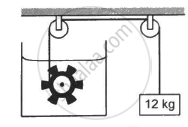
Figure shows a paddle wheel coupled to a mass of 12 kg through fixed frictionless pulleys. The paddle is immersed in a liquid of heat capacity 4200 J K−1 kept in an adiabatic container. Consider a time interval in which the 12 kg block falls slowly through 70 cm. (a) How much heat is given to the liquid? (b) How much work is done on the liquid? (c) Calculate the rise in the temperature of the liquid neglecting the heat capacity of the container and the paddle.
Give one example where high specific heat capacity of water is used as cooling.
Describe a method to determine the specific heat capacity of a solid (say, a piece of copper).
The value of 'γ' for a gas is given as `gamma = 1 + 2/"f"`, where 'f ' is the number of degrees of freedom of freedom of a molecule of a gas. What is the ratio of `gamma_"monoatonic"//gamma_"diatomic"`?
Diatomic gas consists of rigid gas molecules
The molar specific heats of an ideal gas at constant pressure and volume are denoted by Cp and Cv, respectively. If `gamma = "C"_"p"/"C"_"v"` and R is the universal gas constant, then Cv is equal to ______.
