Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What are (i) metals (ii) non-metals, and (iii) metalloids ? Give two examples each of metals, non-metals and metalloids.
Solution
- Metals: Metals are elements that are malleable, ductile and conduct electricity.
Examples: Aluminum and zinc - Non-metals: Non-metals are elements that are neither malleable nor ductile, and they do not conduct electricity. Most non-metals are brittle in nature.
Examples: Phosphorus, hydrogen - Metalloids: Metalloids are elements that show properties of both metals and non metals.
Examples: Germanium, silicon
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An inflated balloon full of air goes down slowly (becomes smaller and smaller slowly) even though the knot at the mouth of the balloon is airtight. And after a week all the air has escaped from the balloon. Explain how the air particles got out of the balloon.
What is meant by saying that metals are sonorous ?
What is the general name of the materials which contain at least two pure substances and show the properties
of their constituents ?
Define a compound. Give two points of evidence to show that sodium chloride is a compound.
One of the following substances is neither a good conductor of electricity nor an insulator. This substance is :
In the following set of substances, one item does not belong to the set. Select this item and explain why it does not belong to the set :
Hydrogen, Oxygen, Steam, Chlorine
State whether the following statement is true or false :
Bread is an example of solid foam.
Define solute.
Define solvent.
Milk of Magnesia is :
One of the following liquids will leave behind a residue on heating. This one is :
One of the following represents the solution of solid in a solid. This one is :
When the solid A is added to water, it dissolves with the evolution of a lot of heat and making little explosions to form two products B and C. The properties of products B and C are entirely different from those of solid A as well as water. Moreover, products B and C cannot be reconverted into solid A and water. When another solid D is added to water, it dissolves with the absorption of a little heat to form a product E which cools down. The product E shows the properties of both, solid D as well as water. Moreover, product E can be converted into solid D and water.
(a) What type of change occurs when solid A is dissolved in water ? Why ?
(b) What type of change occurs when solid D is dissolved in water ? Why ?
(c) Name a metal which you think could behave like solid A. Also name the products B and C.
(d) Name the solid D if it is the one which is used in making ordinary dry cells.
(e) Name the process by which D can be recovered from E.
Name the process by which common salt is obtained from sea-water.
Name the process by which common salt is purified.
Describe the method of separating a mixture containing common salt, sand and ammonium chloride.
Explain how, nitrogen , oxygen and argon gases are separated from air.
Justify your answer.
| Figure 1 | Figure 2 | Figure 3 |
 |
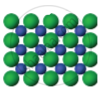 |
 |
The arrangement of particles in three different phases of matter is shown above.
- Which state is represented by Fig. 1?
- In which state will the inter-particle attraction be maximum?
- Which one of them cannot be contained in an open vessel?
- Which one can take the shape of its container?
Atoms or groups of atoms having a charge are called ______.
