Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What are the main steps in aerobic respiration? Where does it take place?
Solution
- Aerobic respiration is a stepwise catabolic process that uses oxygen as the final oxidant and enzymatic regulation to release energy during the complete oxidation of organic food into carbon dioxide and water.
- There are two pathways by which it can occur: the pentose phosphate pathway and the common pathway.
- The first step of the common pathway is called glycolysis because it is shared by anaerobic and aerobic modes of respiration.
- The common pathway of aerobic respiration consists of glycolysis, terminal oxidation, and the Krebs cycle. Within mitochondria, aerobic respiration takes place.
- The final byproduct of glycolysis, pyruvate, is transported from the cytoplasm into the mitochondria.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name the cell organelle in which Krebs’ cycle occurs.
In the oxidative decarboxylation reaction of the citric acid cycle, the following products are observed when α-ketoglutaric acid is oxidized.
During the Krebs cycle, the intermediate α - ketoglutarate is formed as a result of ______
The enzymes needed for Kreb's cycle are located in ______
Which one of the following is the product formed by malic dehydrogenase activity in the Krebs cycle?
Which one of the following reactions is an example of oxidative decarboxylation Krebs cycle?
During Krebs cycle oxalo acetic acid is formed by oxidation of ______.
During Krebs cycle FADH2 is formed in conversion of _____.
Which step of Kreb's cycle involves decarboxylation?
Do you know any step in the TCA cycle where there is substrate level phosphorylation. Which one?
The TCA cycle is an oxidative pathway requiring oxygen for operation. The enzyme which consume oxygen during the operation of the cycle is ______.
Identify X, Y and Z in the given diagram of citric acid cycle and select the correct option.
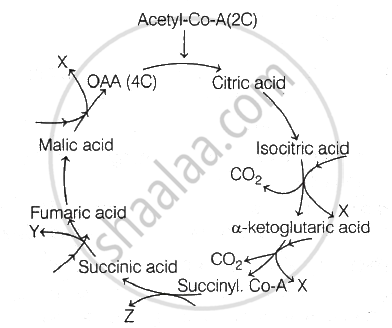
Mitochondrial membrane is not permeable to ______.
