Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is 'excess demand'?
Solution
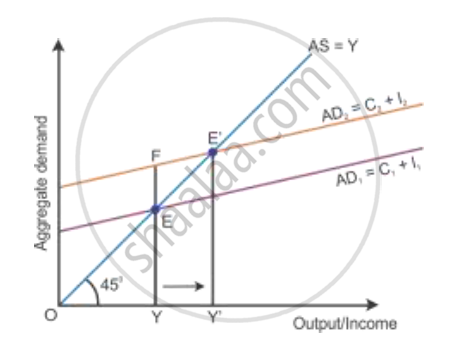
Excess demand occurs in a situation when aggregate demand is more than aggregate supply corresponding to full employment. It leads to the reduction in inventories and inflation in the economy. This situation is considered an inflationary gap—the difference between aggregate demand beyond full employment and aggregate demand at full employment. Aggregate demand is the AD curve and aggregate supply is the AS curve (as shown in the diagram below). While the aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersect each other, the full employment equilibrium is attained at Point E. OY is the full employment level of output, and EY is the aggregate demand at full employment level of output. If the aggregate demand increases beyond the full employment level of output from EY to FY, then the economy will have excess demand (FY − EY = FE).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Reverse Repo Rate
Explain how 'Repo Rate' can be helpful in controlling credit creation.
Explain the role of 'Reverse Repo Rate' in removing it.
Define or explain the following concepts
Repo rate
Distinguish between Any Four of the following :
Bank rate and Interest rate.
State whether the following statement is TRUE or FALSE.
Bank Rate is the selective credit control measure used by the Central Bank of the country.
Define or Explain the following concept.
Bank Rate
Distinguish between:
Bank Rate and Open Market Operations
Write short note on:
Bank Rate
Choose the correct from given options
Repo rate is the rate at which
Based on the passage below, answer the following question.
The Monetary Policy Committee of the Reserve Bank of India kept interest rates on hold Thursday even as it vowed to keep policy sufficiently loose to help revive the coronavirus battered economy. Accepting a key demand of lenders and the corporate sector, the central bank cleared a one-time restructuring of loan accounts to bail out stressed borrowers, including personal, small, and medium loans.
The details of the loan restructuring scheme – expected to kick in after the moratorium on loan repayments ends. August 31 – will be worked out by a committee headed by former ICICI Bank Chairman KV Kamath. The RBI also continued to provide support on the liquidity front and opened a new targeted window for small lenders.
The central bank kept the repo rate unchanged at 4 percent and reduced the reverse repo rate to 3:35 percent.
“The Monetary Policy Committee of the RBI kept interest rates on hold-“. Which of the following is highlighted above by the term ‘interest rates’?
Based on the passage below, answer the following question.
The Monetary Policy Committee of the Reserve Bank of India kept interest rates on hold Thursday even as it vowed to keep policy sufficiently loose to help revive the coronavirus battered economy. Accepting a key demand of lenders and the corporate sector, the central bank cleared a one-time restructuring of loan accounts to bail out stressed borrowers, including personal, small, and medium loans.
The details of the loan restructuring scheme – expected to kick in after the moratorium on loan repayments ends. August 31 – will be worked out by a committee headed by former ICICI Bank Chairman KV Kamath. The RBI also continued to provide support on the liquidity front and opened a new targeted window for small lenders.
The central bank kept the repo rate unchanged at 4 percent and reduced the reverse repo rate to 3:35 percent.
‘Reduction in Repo Rate by RBI’ is likely to ______ the demand for goods and services in the economy.
Explain the role of Repo rate and Reverse Repo rate in correcting deflationary gap in an economy.
Read the following text carefully. Answer the given questions on the basis of the same and common understanding:
| On 30th September 2022, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) raised Repo Rate for the fourth time in a row. The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) decided to raise the policy rate by 50 basis points (1 basis point = `1/100`th of a percent). After this announcement, the new repo rate stands at 5.9%, while the reverse repo rate continues to stand at 3.35%. Commercial banks borrow money from the Central Bank, when there is a shortage of funds. With the surge in the repo rate, borrowings by general public will become costlier. This is because, as RBI hikes its repo rate, it becomes costly for the banks to borrow short term funds from the Central Bank. As a result, the banks hike the rates at which customers borrow money from them to compensate for the hike in the repo rate. This happens because banks offer loans to retail consumers at an interest rate which is generally, directly proportional to the repo rate. The increase of 0.50 percent in repo rate will lead to a higher interest rates on loans for borrowers, implying that the Equated Monthly Instalments (EMIs) for repaying the existing loans will also increase. |
- Define 'Repo Rate'.
- Outline the recent change made by the Monetary Policy Committee of Reserve Bank of India in the repo rate.
- "Increase in repo rate is an important tool used by Monetary Policy Committee to combat the situation of inflation in the Economy." Justify the given statement.
Read the following text carefully. Answer the given questions on the basis of the same and common understanding:
|
On 30th September 2022, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) raised Repo Rate for the fourth time in a row. The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) decided to raise the policy rate by 50 basis points (`1 "basis point" = 1/100`th of a percent). After this announcement, the new repo rate stands at 5.9%, while the reverse repo rate continues to stand at 3.35%. Commercial banks borrow money from the Central Bank, when there i a shortage of funds. With the surge in the repo rate, borrowings by general public will become costlier. This is because, as RBI hikes its repo rate, it becomes costly for the banks to borrow short term funds from the Central Bank. As a result, the banks hike the rates at which customers borrow money from them to compensate for the hike in the repo rate. This happens because banks offer loans to retail consumers at an interest rate which is generally, directly proportional to the repo rate. The increase of 0.50 percent in repo rate will lead to a higher interest rates on loans for borrowers, implying that the Equated Monthly Instalments (EMIs) for repaying the existing loans will also increase. |
- State the meaning of repo rate and reverse repo rate.
- In order to bring down the rate of inflation, outline and discuss the step takes by the Monetary Policy Committee of Reserve Bank of India.
